CAMM (missile family)
CAMM is derived from, and shares some common features and components with, the Advanced Short-Range Air-to-Air Missile (ASRAAM), but with updated electronics, a soft vertical launch system, and an active radar homing seeker.
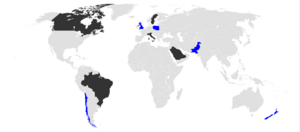
[4][5][6] In the British Army, CAMM forms the interceptor component of the Sky Sabre/Land Ceptor air defence system, which replaced the Rapier missile from 2021.
[11] Brazil announced in 2014 that it was independently to develop the similar 40 kilometres (25 mi)+ ranged MV-AMA (AVibras Medium Altitude Missile) for its Astros 2020 MLRS and naval platforms.
[12] A larger CAMM-MR (medium-range) missile with a range of over 100 kilometres (62 mi) was being developed by the UK and Poland in 2022, to equip Polish Wicher-class frigates and Wisła air defence systems.
[16] FLAADS is intended to deliver a common weapons platform, CAMM, to equip forces in the air, land and maritime environments.
[17][18] During the early stages of the FLAADS programme, requirements were identified for the new missile to meet both current and anticipated threats, namely "airborne targets which are typified by high speed, rapid evasive manoeuvres, low signatures and advanced countermeasure[s].
"[19][20] Phase 1 of the TDP worked on technologies for soft vertical launch, the low-cost active radar seeker, a dual-band two-way data link and a programmable open systems architecture.
[15] Phase 2 began in 2008 and covered the manufacture of flight-worthy subsystems, mid-course guidance firings and captive airborne seeker trials on a Qinetiq Andover experimental aircraft.
Thales' Basingstoke site were also exploring two pilot programs covering missile safety and arming units and intelligent fuzes, in cooperation with MBDA.
[7] Throughout this development, ASRAAM was used as the base design for the future missile but with new software, a turnover pack, folding fins, an RF seeker, and data-link added to facilitate the required capabilities.
Furthermore, MBDA would double production capacity of its Bolton facility in the UK and create a second final assembly line for CAMM-ER in Italy.
[7][10][21] CAMM's software utilises open-systems architecture allowing for both easier integration with new sensors and combat management systems but also general upgrades throughout its service life.
[10] The missiles of the CAMM family can be used interchangeably by both naval and ground-based air defence systems allowing for common usage and shared munition stockpiles between military branches.
[36] It is also fitted with its own power supply allowing it to be dismounted from the parent vehicle and operated remotely if necessary, as well as mounting onboard test-equipment for streamlined maintenance.
[33] CAMM can be integrated on vessels as small as 50 metres (160 ft) such as in/offshore patrol vessels or on larger surface combatants (destroyers and frigates), only requiring the internal installation of the necessary computing systems as well as above-deck aerials for the two-way data link for the missiles, and is designed to be easily integrated with a ship's combat management system.
[58][59] MBDA, as lead contractor, received an £851 million contract to integrate CAMM on the Type 23 frigates with a planned in-service date of November 2016.
Whether it's engaging multiple air threats or fast incoming attack craft, Sea Ceptor represents a massive capability upgrade for the Type 23 frigate.
[6][66] 24x CAMM cells (four 6-cell modules) are expected to be mounted forward of the existing 48-cell Sylver launcher to fulfil the short-range air defence role currently performed by Aster 15 missiles.
[66] CAMM saw its first official combat use with the Royal Navy on the morning of 9 March 2024 when HMS Richmond destroyed two Houthi drones during the Red Sea crisis with an unspecified number of missiles.
[61] Sky Sabre consists of three main components: MBDA iLaunchers loaded with CAMM, the Surface to Air Missile Centre (SAMOC) which runs on Rafael's Modular Integrated C4I Air & Missile Defence System (MIC4AD) as used on Israel's Iron Dome, and Saab's Giraffe Agile Multi-Beam (GAMB) passive-electronically scanned array radar.
The radar itself is raised 12 metres (39 ft) above its parent vehicle to give better detection of low level threats and greater freedom in system deployment by allowing the array to look over obstacles such as buildings or treelines.
"[71] On 1 July 2021, it was revealed that Sky Sabre had started acceptance trials and training with the Royal Artillery and that it would be deployed to the Falkland Islands would occur "late summer/early autumn [2021]".
[81] In March 2022, the UK announced it would be deploying a Sky Sabre fire group to Poland to bolster NATO's Eastern flank following the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine dubbed Operation Stifftail.
[88][53] In July 2023, the UK and Poland with MBDA and PGZ signed agreements that formally began the joint development of the CAMM-MR which would be known as the "Joint/Future Common Missile" with the intention that it would be used by both British and Polish platforms such as on the Wicher-class frigates and possibly Wisła batteries.
[98] On 20 December 2023, Poland signed a $782.5 million deal with the PGZ-NAREW consortium for 24 mobile P-18PL long-range radars for use within both Narew and Wisła with the delivery of all systems expected to be complete by 2035.
[99] In late December 2023, while reporting on developments with the Wicher-class frigates, Naval News confirmed that both CAMM and CAMM-ER would equip the three ship class.
[100] On 29 February 2024, The Polish Armaments Agency announced a $2.53 billion agreement for the delivery and formal integration of IBCS into both the Narew and Wisła systems.