Solar panel
These electrons flow through a circuit and produce direct current (DC) electricity, which can be used to power various devices or be stored in batteries.
Some advantages of solar panels are that they use a renewable and clean source of energy, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and lower electricity bills.
In 1839, the ability of some materials to create an electrical charge from light exposure was first observed by the French physicist Edmond Becquerel.
[1] Though these initial solar panels were too inefficient for even simple electric devices, they were used as an instrument to measure light.
[2] The observation by Becquerel was not replicated again until 1873, when the English electrical engineer Willoughby Smith discovered that the charge could be caused by light hitting selenium.
After this discovery, William Grylls Adams and Richard Evans Day published "The action of light on selenium" in 1876, describing the experiment they used to replicate Smith's results.
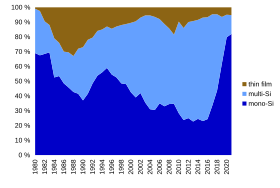
Also, high-cost, high-efficiency, and close-packed rectangular multi-junction (MJ) cells are usually used in solar panels on spacecraft, as they offer the highest ratio of generated power per kilogram lifted into space.
Other commercial applications use rigid thin film solar panels (interleaved between two panes of glass) in some of the world's largest photovoltaic power stations.
Thin-film cells also typically outperform renewable and non-renewable sources for electricity generation in terms of human toxicity and heavy-metal emissions.
[22][23] Ground based mounting supports include: Vertical bifacial solar cells are oriented towards east and west to catch the sun's irradiance more efficiently in the morning and evening.
Even though such installations will not produce the maximum possible average power from the individual solar panels, the cost of the panels is now usually cheaper than the tracking mechanism and they can provide more economically valuable power during morning and evening peak demands than north or south facing systems.
[30] Some special solar PV modules include concentrators in which light is focused by lenses or mirrors onto smaller cells.
This enables the cost-effective use of highly efficient, but expensive cells (such as gallium arsenide) with the trade-off of using a higher solar exposure area.
[34][need quotation to verify] Micro-inverters work independently to enable each panel to contribute its maximum possible output for a given amount of sunlight, but can be more expensive.
Blocking and bypass diodes may be incorporated within the module or used externally to deal with partial array shading, in order to maximize output.
Hence, much of the incident sunlight energy is wasted by solar modules, and they can give far higher efficiencies if illuminated with monochromatic light.
This correlation between the power output of a solar cell and the working temperature of its junction depends on the semiconductor material, and is due to the influence of T on the concentration, lifetime, and mobility of the intrinsic carriers, i.e., electrons and gaps.
The values of these parameters can be found in any data sheet of the photovoltaic module; are the following: - β: VOC variation coefficient with respect to T, given by ∂VOC/∂T.
Techniques for estimating these coefficients from experimental data can be found in the literature[52] The ability of solar modules to withstand damage by rain, hail, heavy snow load, and cycles of heat and cold varies by manufacturer, although most solar panels on the U.S. market are UL listed, meaning they have gone through testing to withstand hail.
[55] Advancements in photovoltaic technologies have brought about the process of "doping" the silicon substrate to lower the activation energy thereby making the panel more efficient in converting photons to retrievable electrons.
[56] Chemicals such as boron (p-type) are applied into the semiconductor crystal in order to create donor and acceptor energy levels substantially closer to the valence and conductor bands.
The degradation index, which is defined as the annual percentage of output power loss, is a key factor in determining the long-term production of a photovoltaic plant.
Given a set of modules exposed to long-term outdoor conditions, the individual degradation of the main electrical parameters and the increase in their dispersion must be considered.
[citation needed] There are several studies dealing with the power degradation analysis of modules based on different photovoltaic technologies available in the literature.
"A dirty solar panel can reduce its power capabilities by up to 30% in high dust/pollen or desert areas", says Seamus Curran, associate professor of physics at the University of Houston and director of the Institute for NanoEnergy, which specializes in the design, engineering, and assembly of nanostructures.
[64] A 2021 study by kWh Analytics determined median annual degradation of PV systems at 1.09% for residential and 0.8% for non-residential ones, almost twice that previously assumed.
[70] Most parts of a solar module can be recycled including up to 95% of certain semiconductor materials or the glass as well as large amounts of ferrous and non-ferrous metals.
These silicon cells are typically 10–20% efficient[86] at converting sunlight into electricity, with newer production models exceeding 22%.
[91] With the rise of global awareness, institutions such as the IRS have adopted a tax credit format, refunding a portion of any solar panel array for private use.
Further, the modules ability to withstand natural environment conditions such as temperature, rain, hail, snow, corrosion, dust, lightning, horizon and near-shadow effects is tested.