Southern Europe
So, the Sirocco hot wind that originates in the heart of the Sahara blows over Italy, going up to the interior of the Alpine arc (Po Valley).
And, conversely, the Alps and the Pyrenees protect the Italian and Iberian Peninsulas from the rains and icy winds from the south of France such as the Mistral and the Tramontane.
Those areas of Mediterranean climate present similar vegetations and landscapes throughout, including dry hills, small plains, pine forests and olive trees.
Cooler climates can be found in certain parts of southern European countries, for example within the mountain ranges of Spain and Italy.
Its colonies later reached the Western Mediterranean, such as Cádiz in Spain and most notably Carthage in North Africa, and even the Atlantic Ocean.
The attacks of the Goths led to the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 AD, a date which traditionally marks the end of the classical period and the start of the Middle Ages.
The period known as the Crusades, a series of religiously motivated military expeditions originally intended to bring the Levant back into Christian rule, began.
The Crusaders would establish trade routes that would develop into the Silk Road and open the way for the merchant republics of Genoa and Venice to become major economic powers.
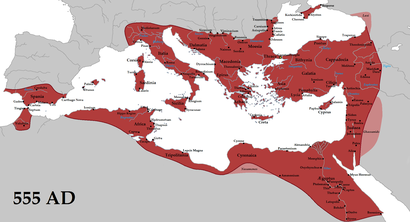
In the Balkans, the Ottoman Empire, a Turkish state originating in Anatolia, encroached steadily on former Byzantine lands, culminating in the fall of Constantinople in 1453.
The Catholic reconquest of Portugal and Spain led to a series of oceanic explorations resulting in the Age of Discovery that established direct links with Africa, the Americas, and Asia.
During this period, Iberian forces engaged in a worldwide struggle with Islamic societies; the battlefronts in this Ibero-Islamic World War stretched from the Mediterranean into the Indian Ocean, finally involving the islands of Southeast Asia (see also: Indo-Mediterranean).
[24] Eventually this ecumenical conflict ended when new players—England, Holland and France—replaced Spain and Portugal as the main agents of European imperialism in the mid-17th century.
[25] The combination of resource inflows from the New World and the Industrial Revolution of Great Britain, allowed a new economy based on manufacturing instead of subsistence agriculture.
The outbreak of World War I in 1914 was precipitated by the rise of nationalism in Southeastern Europe as the Great Powers took up sides.
The Nazi regime under Adolf Hitler came to power in 1933, and along with Mussolini's Italy sought to gain control of the continent by the Second World War.
The countries in the Soviet sphere of influence joined the military alliance known as the Warsaw Pact and the economic bloc called Comecon.
For some of them becoming independent was the major challenge, while others needed to face with poverty and deep dictatorship also Economically, parallel with the political changes, and the democratic transition, – as a rule of law states – the previous command economies were transformed via the legislation into market economies, and set up or renewed the major macroeconomic factors: budgetary rules, national audit, national currency, central bank.
By far the most common Romance languages in southern Europe are Italian (spoken by over 50 million people in Italy, southern Switzerland, Malta, San Marino, and Vatican City) and Spanish, which is spoken by over 40 million people in Spain, Andorra and Gibraltar.
Bosnian-Serbian-Croatian is spoken in Kosovo, Croatia, Serbia, Bosnia, Montenegro, North Macedonia and Italy (in Molise).
As a primary language, however, English has only a small presence in southern Europe, only in Gibraltar (alongside Spanish) and Malta (secondary to Maltese).
[31] Christians in the western half of southern Europe — e.g., Portugal, Spain, Italy — are generally Roman Catholic.
EuroVoc is a multilingual thesaurus maintained by the Publications Office of the European Union, giving definitions of terms for official use.
Countries which belong to the southern/Mediterranean Europe in this classification are:[36] Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Greece, Italy, Malta, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Portugal, Serbia, Slovenia, Spain and Turkey.