Stroke ratio
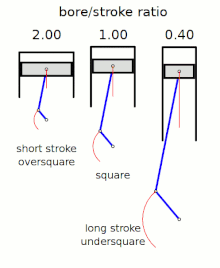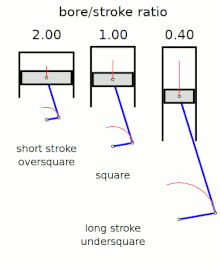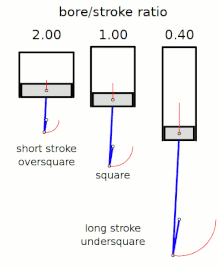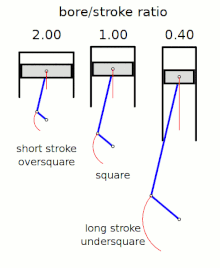
[2] The diameter of the cylinder bore is divided by the length of the piston stroke to give the ratio.
The following terms describe the naming conventions for the configurations of the various bore/stroke ratio: A square engine has equal bore and stroke dimensions, giving a bore/stroke value of exactly 1:1.
Thus an excessively high ratio can lead to a decreased thermal efficiency compared to other engine geometries.
"short stroke engines") are very common, as they allow higher rpm (and thus more power), without excessive piston speed.
This is particularly so in Subaru’s front-engine layout, where the steering angle of the front wheels is constrained by the width of the engine.
Stroke ratios approaching 2.5:1 are allowed,[a] enabling engine speeds of 18,000 rpm while remaining reliable for multiple races.
[8] An engine is described as undersquare or long-stroke if its cylinders have a smaller bore (width, diameter) than its stroke (length of piston travel) - giving a ratio value of less than 1:1.
[clarify][9] Many inline engines, particularly those mounted transversely in front-wheel-drive cars, utilize an undersquare design.
The smaller bore allows for a shorter engine that increases room available for the front wheels to steer.
The 1KR-FE-engine used in the Toyota Aygo, Citroën C1 and Peugeot 107 amongst others is an example of a modern long-stroke engine widely used in FF layout cars.
BMW's acclaimed S54B32 M54 engine was undersquare with a bore and stroke of 87 mm × 91 mm (3.4 in × 3.6 in)), offering a world record torque-per-litre figure (114 N⋅m/L, 1.38 lb⋅ft/cu in) for normally-aspirated production engines at the time; this record stood until Ferrari unveiled the 458 Italia.
The Trojan Car used an undersquare, split piston, two stroke, two-cylinder inline engine; this was partly for this tax advantage and partly because its proportions allowed flexing V-shaped connecting rods for the two pistons of each U-shaped cylinder, which was cheaper and simpler than two connecting rods joined with an additional bearing.
Since the stroke is significantly longer than the bore, the SOHC 16V (2-valve per cylinder) version of this engine is able to generate a peak torque of 350 lb·ft as low as 2501 rpm.
The PW R-2800, Wright R-3350, Pratt & Whitney R-4360 Wasp Major, Rolls-Royce Merlin (1650), Allison V-1710, and Hispano-Suiza 12Y-Z are only a few of more than a hundred examples.