Osteoarthritis
[1] Other symptoms may include joint swelling, decreased range of motion, and, when the back is affected, weakness or numbness of the arms and legs.
[1][2] Risk is greater in those who are overweight, have legs of different lengths, or have jobs that result in high levels of joint stress.
[1] Treatment includes exercise, decreasing joint stress such as by rest or use of a cane, support groups, and pain medications.
[1] Long-term opioid use is not recommended due to lack of information on benefits as well as risks of addiction and other side effects.
Stiffness is most common in the morning, and typically lasts less than thirty minutes after beginning daily activities, but may return after periods of inactivity.
[13] Some people report increased pain associated with cold temperature, high humidity, or a drop in barometric pressure, but studies have had mixed results.
[22] Changes in sex hormone levels may play a role in the development of osteoarthritis, as it is more prevalent among post-menopausal women than among men of the same age.
[37][38] Collagen fibres exert the compressive force, whereas the Gibbs–Donnan effect and cartilage proteoglycans create osmotic pressure which tends to draw water in.
New bone outgrowths, called "spurs" or osteophytes, can form on the margins of the joints, possibly in an attempt to improve the congruence of the articular cartilage surfaces in the absence of the menisci.
[55] In 1990, the American College of Rheumatology, using data from a multi-center study, developed a set of criteria for the diagnosis of hand osteoarthritis based on hard tissue enlargement and swelling of certain joints.
EOA is a much less common, and more aggressive inflammatory form of osteoarthritis which often affects the distal interphalangeal joints of the hand and has characteristic articular erosive changes on X-ray.
[88] Among people with hip and knee osteoarthritis, exercise in water may reduce pain and disability, and increase quality of life in the short term.
[91] A 2003 Cochrane review of 7 studies between 1969 and 1999 found ice massage to be of significant benefit in improving range of motion and function, though not necessarily relief of pain.
[101] Education is helpful in self-management of arthritis, and can provide coping methods leading to about 20% more pain relief when compared to NSAIDs alone.
[106] A 2018 meta-analysis found that oral collagen supplementation for the treatment of osteoarthritis reduces stiffness but does not improve pain and functional limitation.
A Cochrane review from 2016 concluded that reasonably reliable evidence is available only for use of topical diclofenac and ketoprofen in people aged over 40 years with painful knee arthritis.
[110] Use of analgesia, intra-articular cortisone injection and consideration of hyaluronic acids and platelet-rich plasma are recommended for pain relief in people with knee osteoarthritis.
[112] Local drug delivery by intra-articular injection may be more effective and safer in terms of increased bioavailability, less systemic exposure and reduced adverse events.
[125] Injection of beta particle-emitting radioisotopes (called radiosynoviorthesis) is used for the local treatment of inflammatory joint conditions.
[135] If the impact of symptoms of osteoarthritis on quality of life is significant and more conservative management is ineffective, joint replacement surgery or resurfacing may be recommended.
[144] People undergoing a joint transplant (osteochondral allograft) do not need to take immunosuppressants as bone and cartilage tissues have limited immune responses.
[148][149] There is some low-quality evidence that indicates that when comparing total shoulder arthroplasty over hemiarthroplasty, no large clinical benefit was detected in the short term.
[169] A 2014 Cochrane review found that while ASU might help relieve pain in the short term for some people with osteoarthritis, it does not appear to improve or maintain the health of affected joints.
[167] The review noted a high-quality, two-year clinical trial comparing ASU to chondroitin – which has uncertain efficacy in osteoarthritis – with no difference between the two agents.
[182] Further research is needed to determine if balnotherapy for osteoarthritis (mineral baths or spa treatments) improves a person's quality of life or ability to function.
[184] There is low quality evidence that therapeutic ultrasound may be beneficial for people with osteoarthritis of the knee; however, further research is needed to confirm and determine the degree and significance of this potential benefit.
[191] In the Middle East and North Africa from 1990 to 2019, the prevalence of people with hip osteoarthritis increased three–fold over the three decades, a total of 1.28 million cases.
Osteoarthritis has been reported in several species of animals all over the world, including marine animals and even some fossils; including but not limited to: cats, many rodents, cattle, deer, rabbits, sheep, camels, elephants, buffalo, hyena, lions, mules, pigs, tigers, kangaroos, dolphins, dugong, and horses.
[215] A study conducted by scientists at the University of Twente found that osmolarity induced intracellular molecular crowding might drive the disease pathology.
[218][219] A 2015 systematic review of biomarkers for osteoarthritis looking for molecules that could be used for risk assessments found 37 different biochemical markers of bone and cartilage turnover in 25 publications.




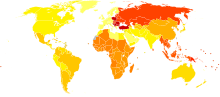
|
no data
≤ 200
200–220
220–240
240–260
260–280
280–300
|
300–320
320–340
340–360
360–380
380–400
≥ 400
|