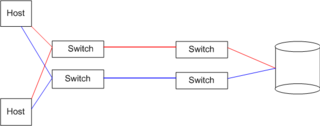
Switched fabric
The generation of high-speed serial data interconnects that appeared in 2001–2004 which provided point-to-point connectivity between processor and peripheral devices are sometimes referred to as fabrics; however, they lack features such as a message-passing protocol.
[citation needed] For example, HyperTransport, the computer processor interconnect technology, continues to maintain a processor bus focus even after adopting a higher speed physical layer.
Visibility among devices (called nodes) in a fabric is typically controlled with Fibre Channel zoning.
Most Fibre Channel network designs employ two separate fabrics for redundancy.
The fabric topology allows the connection of up to the theoretical maximum of about 16 million devices, limited only by the available address space (224).