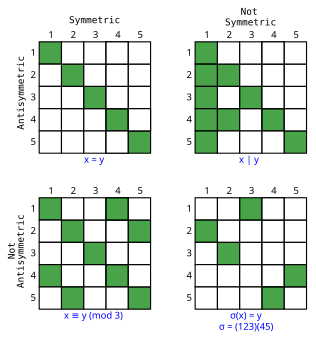
Symmetric relation
All definitions tacitly require the homogeneous relation
A term's definition may require additional properties that are not listed in this table.
Formally, a binary relation R over a set X is symmetric if:[1] where the notation aRb means that (a, b) ∈ R. An example is the relation "is equal to", because if a = b is true then b = a is also true.
[2] Symmetry, along with reflexivity and transitivity, are the three defining properties of an equivalence relation.
However, a relation can be neither symmetric nor asymmetric, which is the case for "is less than or equal to" and "preys on").