Amiga software
[2][ 3][ 4] New applications for the three existing Amiga-like operating systems[5] are generally ported from the open source (mainly from Linux) software base.
Both were used by Andy Warhol to produce a black-and-white photo of Debbie Harry at the Launch Gala at Lincoln Center, New York City in July 1985[6].
In 1985 Commodore licensed the software called Transformer from Simile Research and put it on the market in January 1986, bundled with an external A1020 5.25-inch floppy drive.
AmigaBasic from Microsoft, VizaWrite, TextCraft (word processors), Pagesetter (Desktop Publishing), Analyze!
It was the first rendering tool available for the first time to a vast audience of public, and in October of the same year, Impulse released TurboSilver.
In July, Wordperfect created an "Amiga/Atari Division" and started selling a version of its word processor for the Commodore platform for US$400[11].
It could load and save Wordperfect files created on any platform, such as IBM, Macintosh and Apple II.
[12] Wordperfect 4.1 for the Amiga was the first word processor in the world capable of opening an unlimited number of documents (limited by RAM), each in a separate window.
[13] In 1987, Andrew Tanenbaum released Minix, a free version of Unix with complete source code.
[citation needed] At COMDEX NewTek showed for the first time a prototype of Video Toaster and Impulse released TurboSilver 2.0.
It allowed digital painting using HAM graphics mode and the full 4096-color palette of Amiga on a single screen.
Maxiplan 500 become Maxiplan 1.x, Electronic Arts showed DeLuxe Photo Lab (photo editing software), Newtek demonstrated DigiView 3.0 hardware and software image digitizing suite, and WordPerfect released the WordPerfect Library for the Amiga.
Gold Disk released ComicSetter (comic creation) and MovieSetter (32-color cartoons with stereo sound animation software).
In November, at the World of Commodore Show, ReadySoft demonstrated its Amax Macintosh emulator for the Amiga.
Running under AmigaDos it used a custom screen to allow users access to X Window programs on other Amigas as well as non-Amiga systems on the local network.
Amiga created utilities for hard disk partitioning; diagnostic tools; VGA promoting tools for ancient Amiga software with TV resolution graphic screens; game loaders for storing and auto-loading from hard disks, auto-starting non-standard floppy disks; disk copiers; backup and recovery tools, archive and compression utilities; command line interfaces and text-based shells; graphical GUI interfaces with WIMP paradigm; advanced graphics systems; PostScript; fonts; font design; audio system; native, external, widely common used, and third-party filesystems; MultiView; MIME types; USB stacks; Firewire stacks (IEEE 1394); printer drivers; video digitizers; graphic tablets; scanner drivers; genlocks, chroma-key, signal video inverters; infrared devices and remote controls; WiFi and Bluetooth devices; and special devices.
Solutions include modem software, Direct Connect, BBS managing, Fidonet, Packet Radio; Prestel, Videotel, Videotex, Minitel; Teletext, Televideo, Viewdata; FAX, answering machine and voice mail; ISDN; networking and Ethernet protocols; World Wide Web (TCP/IP stacks, browsers, E-mail programs, newsreaders, Internet Radio, proxy server support programs, PPP, Telnet, podcasting, RSS feed, Distributed Net, Google Services, Instant Messaging and chat, FTP and FTP server, weather casting news, Webcam supporting, clock synchronization, SMS Short Messages, Web development and HTTP server, Peer2Peer, VCast (online VCR), YouTube, Flash player, monitoring webpages, Remote Desktop, SSL, SSH, et cetera); communication protocols.
Minitel had many consumer-level communication services, including chatting, email, railway and broadcast timetables and travel and hotel booking.
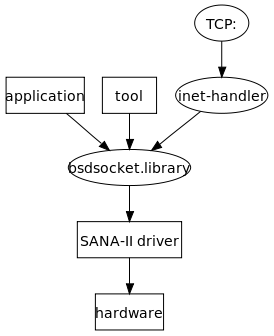
Amiga supported SANA-II and MNI drivers, Envoy protocols from IAM, AS225, AS225r2 TCP-IP from Commodore, DECnet, Novell NetWare through Amiga Client for Novell NetWare, Quicknet fast proprietary peer to peer protocol, AppleTalk through emulators.
BurnIt!, Frying Pan, MakeCD, AmiDVD, DVDRecord, DVDAuthor could burn CDs, DVDs and/or Blu-ray media.
BlueHD from German programmer Carsten Siegner is a MorphOS program capable of authoring and burning HD-DVDs in these formats: (A complete list of ISO managements and converters is available on Aminet.)
It became popular in 1989–1990, due to the NeXT computer, that used the same 68030 processor as Amiga 3000) and that it also had the Acorn Archimedes RISC OS docking station utility.
Because the custom chipset shares RAM (and therefore the memory bus) with the CPU, throughput increases measurably if the display is disabled.
(PC Engine, TurboGrafx-16),[39] FunnyMu (Creativision, Funvision, Wizzard), AmiArcadia (Arcadia 2001 and VC 4000, TVGC).
Because Amiga was one of the first game-oriented computers to feature a built-in floppy disk drive, it simplified software piracy.
[citation needed] Anti-piracy measures included the practice of distributing software on disks that contained secret "keys" on high-numbered tracks that were officially unused.
Pirates responded with "cracking" software that altered the code to bypass copy protection completely.
Early implementations wrote to a video display register, causing it to break into multiple segments of colorful noise, which would become finer as the decrunching continued.
TransADF is a program that transfers the contents of a floppy disk or a similar block device to a file.
[40][41] This program can compress the disk image using the popular deflate algorithm, as utilized by PKZip and gzip, amongst others.