TETRA
As well as allowing direct communications in situations where network coverage is not available, DMO also includes the possibility of using a sequence of one or more TETRA terminals as relays.
In addition to voice and dispatch services, the TETRA system supports several types of data communication.
It is also possible for the terminal to act as a one-to-one walkie talkie but without the normal range limitation since the call still uses the network.
To overcome the limitations many software vendors have begun to consider hybrid solutions where TETRA is used for critical signalling while large data synchronization and transfer of images and video is done over 3G / LTE.
Speech signals in TETRA are sampled at 8 kHz and then compressed with a vocoder using algebraic code-excited linear prediction (ACELP).
This data stream is error-protection encoded before transmission to allow correct decoding even in noisy (erroneous) channels.
A single slot consists of 255 usable symbols, the remaining time is used up with synchronisation sequences and turning on/off, etc.
The downlink (i.e., the output of the base station) is normally a continuous transmission consisting of either specific communications with mobile(s), synchronisation or other general broadcasts.
Riess[10] mentions in early TETRA design documents that encryption should be done with a stream cipher, due to the property of not propagating transmission errors.
A total of 5 flaws were filed to the CVE database:[15] In addition, the Midnight Blue team spots a "peculiarity regarding the TEA3 S-box", but has yet to determine whether it constitutes a weakness.
The Midnight Blue team gained access to TETRA's cryptographic code by attacking the trusted execution environment on a TETRA-enabled radio.
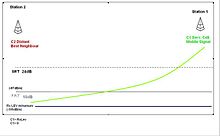
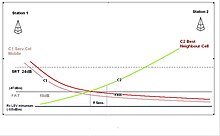
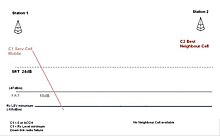
These are represented in association with the decaying radio carrier as the distance increases from the TETRA base station.
From this illustration, these SRT and FRT triggering points are associated to the decaying radio signal strength of the respective cell carriers.
When the FRT threshold is breached, the MS is in a situation where it is essential to relinquish (or abandon) the serving cell and obtain another of at least usable quality.
Cell reselection procedures are then activated in order to find a suitable radio base station.
For dexterity, flexibility, and evolution ability, the public transportation radio engineering department, have chosen to use the open sources, Java language specification administered by Sun and the associated work groups in order to produce a transport application tool kit.
The advantage being that each of the end users may attach themselves to any given terminal, and group for short durations without requiring any major reconfiguration by means of radio software programming tools.
Similarly, the aggression feature functions, but with a higher tone frequency (880 Hz), and with a quicker repetitious nature, so to highlight the urgency of the alert.
The parameters tab provides an essential means to the terminal end-user allowing them to pre-configure the target (preprogrammed ISSI or GSSI ) destination communication number.
With this pre-programmed destination number, the end-user shall liaise with the destination radio terminal or roll allocation server, and may communicate, in the group, or into a dedicated server to which the service acquisition requests are received, preprocessed, and ultimately dispatched though the TETRA core network.
The parameters tab also provides a means of choosing between preselected tones to match the work group requirements for the purposes of fraud and aggression alerts.
TEDS performance is optimised for wideband data rates, wide area coverage and spectrum efficiency.
[18] Advances in DSP technology have led to the introduction of multi-carrier transmission standards employing QAM modulation.
At the end of 2009[update] there were 114 countries using TETRA systems in Europe, Middle East, Africa, Asia Pacific, Caribbean and Latin America.
In 2016, TETRA trunking radio expanded to Haina and San Cristobal, cities in the southwest of Santo Domingo.
The perceived higher audio quality compared to other digital voice modes, capacity for packet data, SDS, single frequency DMO repeaters, close proximity of the UHF (430-440MHz) amateur radio band and full duplex audio in TMO are motivating arguments to experiment contacts with this technology.
Additionally, an open-source project aims to create a complete SDR-based TETRA stack, with a working DMO repeater proof of concept.