Theca of follicle
They have many diverse functions, including promoting folliculogenesis and recruitment of a single follicle during ovulation.
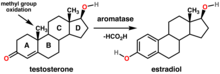
[3] FSH induces the granulosa cells to synthesize aromatase, an enzyme that converts the androgens made by the theca interna into estradiol.
In human adult females, the primordial follicle is composed of a single oocyte surrounded by a layer of closely associated granulosa cells.
In early stages of the ovarian cycle, the developing follicle acquires a layer of connective tissue and associated blood vessels.
As development of the secondary follicle progresses, granulosa cells proliferate to form the multilayered membrana granulosum.