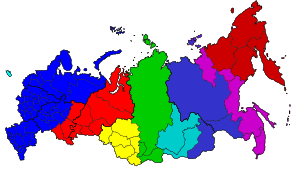
Time in Russia
Since 27 December 2020, the time zones are as follows:[1][2][3] Prior to 2011, Russia moved its clocks backward and forward on the same annual cycle as Europe.
On 27 March 2011, clocks were advanced as usual, but they did not go back on 30 October 2011, effectively making Moscow Time UTC+04:00 permanently.
[5] On 26 October 2014, following another change in the law, the clocks in most of the country were moved back one hour, but summer daylight saving time was not reintroduced; Moscow Time returned to UTC+03:00 permanently.
1867 at 3:30 p.m. GMT+14:59 in the capital of New Archangel (Sitka) (00:31 GMT), Alaska belonged to Russia (Russian America) which used the Julian calendar, which was 11 or 12 days behind the Gregorian calendar (as used by the rest of Russia) and had local times up to GMT+15:10.
The westernmost area of Russia was Congress Poland, with local times down to GMT+01:10.
On 27 March 1988, 02:00:00, Saratov and Volgograd oblasts changed its time zone from MSK+1 to MSK.
Although the Russian government wanted to reduce the number of time zones even further, there were protests in far-eastern Russia on the changes, including a 20,000-strong petition in support of Kamchatka returning to UTC+12:00.
[28] On 29 May 2016, Tomsk Oblast moved forward one hour from UTC+06:00 to UTC+07:00 (from Omsk to Krasnoyarsk time).
[29] On 24 July 2016, Novosibirsk Oblast moved forward one hour from UTC+06:00 to UTC+07:00 (from Omsk to Krasnoyarsk time).
[30] On 4 December 2016, Saratov Oblast moved forward one hour from UTC+03:00 to UTC+04:00 (from Moscow to Samara time).
[31][32] On 28 October 2018, Volgograd Oblast moved forward one hour from UTC+03:00 to UTC+04:00 (from Moscow to Samara time),[33] but this change was reverted on 27 December 2020.
[34][35] After the Russian annexation of Donetsk, Kherson, Luhansk and Zaporizhzhia oblasts in September 2022, the parts of these oblasts under Russian administration remained on Moscow Time (UTC+03:00) and did not revert to UTC+02:00 with the rest of Ukraine at the end of its daylight saving time period in October 2022.
The list below shows the 16 zones for Russia as defined in the file zone.tab of the database.
On the last Sunday in October 2011, daylight-saving time ended in tzdata, but all zones moved forward one hour.

| KALT | Kaliningrad Time | UTC+2 | (MSK−1) | |
| MSK | Moscow Time | UTC+3 | (MSK±0) | |
| SAMT | Samara Time | UTC+4 | (MSK+1) | |
| YEKT | Yekaterinburg Time | UTC+5 | (MSK+2) | |
| OMST | Omsk Time | UTC+6 | (MSK+3) | |
| KRAT | Krasnoyarsk Time | UTC+7 | (MSK+4) | |
| IRKT | Irkutsk Time | UTC+8 | (MSK+5) | |
| YAKT | Yakutsk Time | UTC+9 | (MSK+6) | |
| VLAT | Vladivostok Time | UTC+10 | (MSK+7) | |
| MAGT | Magadan Time | UTC+11 | (MSK+8) | |
| PETT | Kamchatka Time | UTC+12 | (MSK+9) |