Tornadoes of 2009
Strong and destructive tornadoes form most frequently in the United States, Argentina, Brazil, Bangladesh, and Eastern India, but can occur almost anywhere under the right conditions.
Tornadoes also develop occasionally in southern Canada during the Northern Hemisphere's summer and somewhat regularly at other times of the year across Europe, Asia, Argentina, Australia and New Zealand.
Worldwide, 73 fatalities were caused by tornadoes; 22 in the United States, 20 in India, 11 in Argentina, eight in the Philippines, four each in Canada and Brazil, two in Greece and one each in Serbia and Russia.
May started quite active, but in a rather unusual pattern as most tornadoes in the early part of the month were due to summer-like derechos as opposed to large-scale supercells.
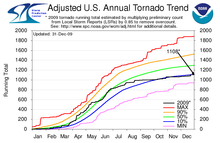
Without any landfalling tropical cyclones in the Atlantic and a relatively stable air mass, September was extremely quiet with only a very small number of isolated weak tornadoes.
[7] For February 10, the Storm Prediction Center issued a moderate risk for severe weather for portions of eastern Oklahoma, northeastern Texas, western Arkansas, and northwest Louisiana.
[18] The Storm Prediction Center also issued a very large slight risk area for February 11 which encompassed parts of the Deep South, Ohio Valley, Midwest, and Appalachians.
[7] Strong southwesterly winds transported a moist air mass northeastward across the Gulf Coast states and the Tennessee Valley.
The moisture combined with daytime heating to support a moderately unstable air mass in advance of a cold front, which pushed southeastward across the Tennessee Valley and Gulf States during the afternoon and evening.
[21] As a result, a moderate risk of severe weather was issued by the Storm Prediction Center for portions of Louisiana, Mississippi, Alabama, Georgia and the Florida Panhandle.
In Newton County, 20 to 30 homes in a heavily wooded subdivision were damaged by trees blown down by an EF1 tornado that was on the ground for 2 miles (3.2 km).
[26] At 7:40 a.m CST (1340 UTC) rain fell from the sky and an EF0 tornado blew down several trees and power lines and destroyed two outbuildings in southern Tallapoosa County.
A cold front combined with the low moved across the central and southern Great Plains and was the main area where thunderstorm development would occur.
[38] During the day, a fast-moving supercell produced several tornadoes in eastern Nebraska and across the state line into the west central portion of Iowa.
[7] A moderate risk of severe weather was issued for a large area of the southern United States from the Mississippi Delta to northeast Florida.
[66] As a result, a moderate risk of severe weather was issued by the Storm Prediction Center for eastern Oklahoma, southeast Kansas, southwest Missouri and western Arkansas.
[72] The Storm Prediction Center issued a moderate risk of severe weather for sections of the Tennessee Valley, Gulf Coast states and into the southern Appalachians region.
[73] As the system moved across the lower Ohio Valley area, a line of thunderstorms started to produce tornadoes in parts of Kentucky and Tennessee.
[93] In a separate storm (though part of the same low-pressure system), another F0 tornado was confirmed in Windsor, Ontario damaging the roof of a CUPE union hall building.
[94] On the morning of April 26, a high risk of severe weather was issued for much of Oklahoma into southern Kansas, where a major tornado outbreak was expected along the dryline.
A well documented event took place northeast of Lubbock near the town of Cedar Hill where several tornadoes touched down from a single storm.
[97] On May 3, a moderate risk of severe weather was issued for parts of Mississippi, Alabama, and Georgia, mainly for a threat of intense downburst winds.
[126][127] A tornado that lasted five minutes hit Cantavir, a village in the province of Vojvodina, killing a nine-year-old boy, injuring several people and damaging more than 500 households.
[144] The tornado downed power lines, nearly destroyed a dog food factory as it passed very close to the structure, and damaged several homes before dissipating.
One tornado, rated F2 on the Fujita Scale, struck a fishing lounge, uprooting two cabins and dropping the buildings into a lake near Ear Falls, Ontario, resulting in three deaths and at least five others injured.
At 1:50 pm CDT, an EF0 tornado touched down in south Minneapolis, Minnesota, uprooting trees and causing minor structural damage.
In the Woodbridge and Maple areas of Vaughan just northwest of Toronto, the mayor declared a state of emergency for the city, 175 homes were evacuated because of heavy structural damage and some of those houses have been condemned, only minor injuries.
The deadliest tornado, rated F4[citation needed], touched down in the Misiones Province, passing near the towns of Tobuna and San Pedro.
[4] After a very long lull in activity, severe weather developed again across parts of the Southern United States as a strong cold front moved through.
Severe activity was limited to the immediate coastal area with supercells embedded within the larger squall line, where a single EF0 tornado was reported.