Uhuru (satellite)
It performed the first comprehensive survey of the entire sky for X-ray sources, with a sensitivity of about 0.001 times the intensity of the Crab nebula.
The main objectives of the mission were:[2] The payload consisted of two sets of proportional counters, each with ~0.084 m2 effective area.
The lower energy limit was determined by the attenuation of the beryllium windows of the counter plus a thin thermal shroud that was needed to maintain temperature stability of the spacecraft.
Pulse-shape discrimination and anticoincidence techniques were used to filter out emissions of particles and undesirable high-energy photons in the background.
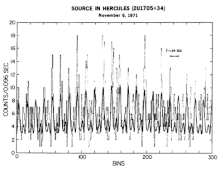
[2] Uhuru achieved several outstanding scientific advances, including the discovery and detailed study of the pulsing accretion-powered binary X-Ray sources such as Cen X-3, Vela X-1, and Her X-1, the identification of Cygnus X-1, the first strong candidate for an astrophysical black hole, and many important extragalactic sources.