Underwater orienteering
Firstly, all of the scuba equipment and instruments are usually mounted together in a housing to create a streamlined form that can be held in front of the competitor to reduce resistance whilst swimming underwater and with a bracket to locate the instruments in front of the competitor allowing use whilst swimming and navigating the event courses.
Competition sites are not permitted to be located in shipping lanes and areas intended for boating and swimming activity.
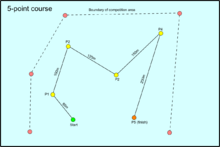
Competitors are required to swim underwater around the rounding buoys in sequence and cross the finish line within the time limit of 15 minutes 20 seconds.
Competitors are ranked using a point scoring system for correctly rounding the three buoys and for course accuracy at the finish line.
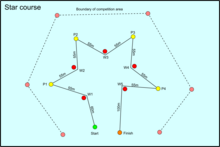
Competitors are required to swim underwater around the course in sequence and to confirm the discovery of each orienteering point ‘by clearly pulling or spinning it’.
Competitors are required to swim underwater around the course in sequence and to confirm the discovery of each orienteering point ‘by clearly pulling or spinning it’.
[11] The Monk Competition is an event where a team of two competitors is required whilst underwater to plan and then navigate from the start to the finish of the course via a number of orienteering points (also called control points) shown on a waterproof map provided at the start of the event within a maximum time of 18 minutes.
The map contains details of the shore lines, boundary of the competition area, and the exact position of start, finish and the control points to be located.
[16] As of May 2013, the following countries and territories have affiliated with the Commission - Austria, Belgium, Bosnia-Herzegovina, Croatia, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Egypt, Estonia, France, Germany, Hong Kong, Hungary, Italy, Japan, Kazakhstan, Montenegro, Russia, Serbia, Slovenia, South Africa, Spain and Ukraine.
The first international competition was held in Crimea during 1965 with participants attending from Austria, Bulgaria, Hungary, Italy and the USSR.
Within Central Europe, the first competitions were held in Angera on Lake Maggiore in Italy during 1961 and at Wörthersee in Austria during 1962.
The M Course was substantially revised in the proposed international rules tabled by the USSR at the CMAS General Assembly in 1969 with a change from precision to speed by the introduction of the points system.