Unitary state
The central government may create or abolish administrative divisions (sub-national or sub-state units).
The war accelerated the process of transforming France from a feudal monarchy to a unitary state.
A large majority of the UN member countries, 166 out of 193, have a unitary system of government, while significant population and land mass is under some kind of federation.
This means that the sub-national units have a right to existence and powers that cannot be unilaterally changed by the central government.
Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland have a degree of autonomous devolved power, but such power is delegated by the Parliament of the United Kingdom, which may enact laws unilaterally altering or abolishing devolution.
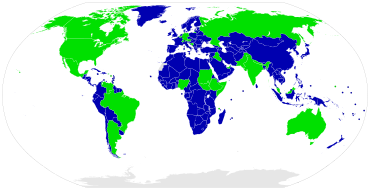
Unitary states