Uptime
Uptime is a measure of system reliability, expressed as the period of time a machine, typically a computer, has been continuously working and available.
[2][3] Although that might sound unusual, that is actually common when servers are maintained under an industrial context and host critical applications such as banking systems.
A server running Novell NetWare has been reported to have been shut down after 16 years of uptime due to a failing hard disk.
Uptime can be determined via Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI), by querying the LastBootUpTime property of the Win32_OperatingSystem class.
WMI can also be queried using a variety of application programming interfaces, including VBScript or PowerShell.
[12][13] Microsoft formerly provided a downloadable utility called Uptime.exe, which reports elapsed time in days, hours, minutes, and seconds.
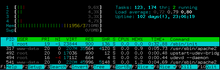
[16] On multi-core systems (and some Linux versions) the second number is the sum of the idle time accumulated by each CPU.
[21] The command output above shows that node JACK on 29 January 2008 at 16:32:04.67 has an uptime of 894 days 22 hours 28 minutes and 52 seconds.