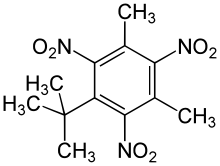
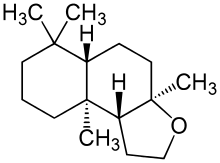
Synthetic musk
An artificial musk was obtained by Albert Baur in 1888 by condensing toluene with isobutyl bromide in the presence of aluminium chloride, and nitrating the product.
The creation of this class of musks was largely prompted through the need for eliminating the nitro functional group from nitro-musks due to their photochemical reactivity and their instability in alkaline media.
This led to the eventual discovery of phantolide, so named due to its commercialization by Givaudan without initial knowledge of its chemical structure (elucidated 4 years later).
While poorer in smell strength, the performance and stability of this compound class in harsh detergents led to its common use, which spurred further development of other polycyclic musks including Galaxolide.
The first compound of this class was introduced 1975 with Cyclomusk, though similar structures were noted earlier in citronellyl oxalate and Rosamusk.