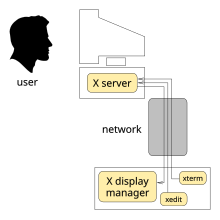
X terminal
X terminals enjoyed a period of popularity in the early 1990s when they offered a lower total cost of ownership alternative to a full Unix workstation.
This connects to an X display manager (introduced in X11R3) running on a central machine, using XDMCP (X Display Manager Control Protocol, introduced in X11R4).
[1][page needed] Thin clients have somewhat supplanted X terminals in that they are equipped with added flash memory and software for communication with remote desktop protocols.
In the early 1990s, several vendors introduced X terminals including HP, DEC (including the VT1000 series), IBM, Samsung, NCD, Gipsi,[2] Tektronix,[3] and Visual Technology.
You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.This computer networking article is a stub.