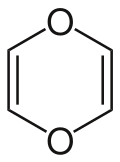
1,4-Dioxin
dithiin 1,4-Dioxin (also referred as dioxin or p-dioxin) is a heterocyclic, organic, non-aromatic[2] compound with the chemical formula C4H4O2.
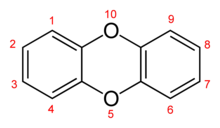
Because of their extreme importance as environmental pollutants, current scientific literature uses the name dioxins commonly for simplification to denote the chlorinated derivatives of dibenzo-1,4-dioxin, more precisely the polychlorinated dibenzodioxins (PCDDs), among which 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzodioxin (TCDD), a tetrachlorinated derivative, is the best known.
The polychlorinated dibenzodioxins, which can also be classified in the family of halogenated organic compounds, have been shown to bioaccumulate in humans and wildlife due to their lipophilic properties, and are known teratogens, mutagens, and carcinogens.
[4] Famous PCDD exposure cases include Agent Orange sprayed over vegetation by the British military in Malaya during the Malayan Emergency and the U.S. military in Vietnam during the Vietnam War, the Seveso disaster, and the poisoning of Viktor Yushchenko.
Polychlorinated dibenzofurans are a related class compounds to PCDDs which are often included within the general term "dioxins".