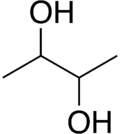
2,3-Butanediol
It exists as three stereoisomers, a chiral pair and the meso isomer.
2,3-Butanediol is prepared by hydrolysis of 2,3-epoxybutane:[3] The isomer distribution depends on the stereochemistry of the epoxide.
[3] The (2R,3R)-stereoisomer of 2,3-butanediol is produced by a variety of microorganisms in a process known as butanediol fermentation.
[4] It is found naturally in cocoa butter, in the roots of Ruta graveolens, sweet corn, and in rotten mussels.
[5] During World War II research was done towards producing 2,3-butanediol by fermentation in order to produce 1,3-butadiene, the monomer of the polybutadiene used in a leading type of synthetic rubber.