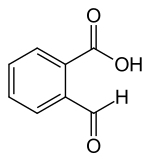
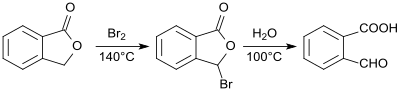
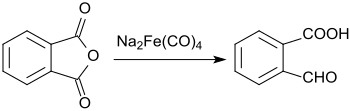
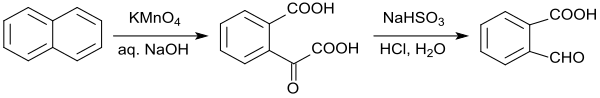
2-Carboxybenzaldehyde
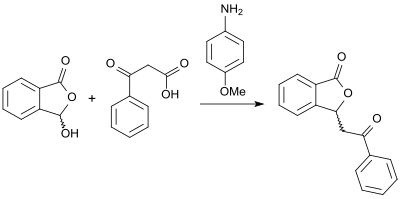
[13] An alternative approach to (racemic) 3-substituted phthalides with high yields is opened up by the reaction of 2-carboxybenzaldehyde and β-keto acids in the presence of base 4-anisidine in glycerol as solvent.
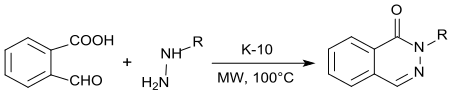
[15] Phthalazinones (1(2H)-phthalenazinones) are important building blocks for natural products, fine chemicals and pharmaceutical active ingredients,[16] such as the antihypertensive vasodilator hydralazine.
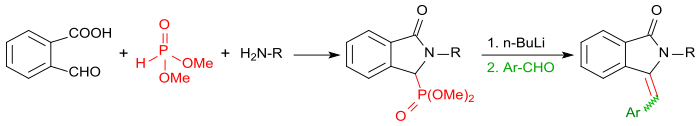
[18] Another three-component reaction (here carried out as a Strecker synthesis) with 2-carboxybenzaldehyde, primary amines and potassium cyanide in methanol yields in the acidic medium an N-substituted isoindolinone-1-carbonitrile, formally an aminoacetonitrile derivative of isoindolinone with two moles of HCN.
[20] The isochromenones obtained are quantitatively converted into isoindolinones by reacting in DMSO upon ring constriction into substituted isobenzofurans or with catalytic amounts of iodine in triethylamine.
[21] With isonitriles instead of potassium cyanide, 2-carboxybenzaldehyde and primary aromatic amines react in methanol to form substituted isochromen-1-ones, which are converted to isoindolinones with traces of acid.
[22] Synthesis pathways for the isoquinoline derivative[23] quinisocaine[24] (acting as a local anesthetic) and the antihistamine azelastine[25] are also based on 2-carboxybenzaldehyde as starting material.