(523622) 2007 TG422
(523622) 2007 TG422 (provisional designation 2007 TG422) is a trans-Neptunian object on a highly eccentric orbit in the scattered disc region at the edge of Solar System.
Approximately 260 kilometers (160 miles) in diameter, it was discovered on 3 October 2007 by astronomers Andrew Becker, Andrew Puckett and Jeremy Kubica during the Sloan Digital Sky Survey at Apache Point Observatory in New Mexico, United States.
[1] According to American astronomer Michael Brown, the bluish object is "possibly" a dwarf planet.
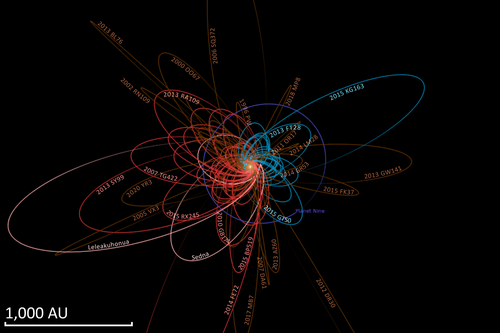
[7] It belongs to a group of objects studied in 2014, which led to the proposition of the hypothetical Planet Nine.
[7] According to the Johnston's archive and to Michael Brown, 2007 TG422 measures 222 and 331 kilometers in diameter, based on an absolute magnitude of 6.5 and an assumed standard albedo of 0.09 and 0.04 for the body's surface, respectively.