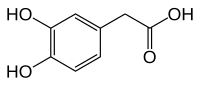
3,4-Dihydroxyphenylacetic acid
3,4-Dihydroxyphenylacetic acid (DOPAC) is a metabolite of the neurotransmitter dopamine.
Both of these substances are degraded to form homovanillic acid (HVA).
Both degradations involve the enzymes monoamine oxidase (MAO) and catechol-O-methyl transferase (COMT), albeit in reverse order: MAO catalyzes dopamine to DOPAC, and COMT catalyzes DOPAC to HVA; whereas COMT catalyzes dopamine to 3-MT and MAO catalyzes 3-MT to HVA.
The third metabolic end-product of dopamine is norepinephrine (noradrenaline).
[1] This product has been synthesized (52% yield) from 4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid via aerobic biotransformation using whole cell cultures of Arthrobacter protophormiae.