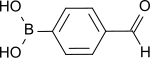
4-Formylphenylboronic acid
Reaction with tri-n-butyl borate leads to the protected aryl boronic ester which gives after acidic work-up the target product in 78% yield.
The same reactants are forming with the aryl boronic ester at -60 °C 4-formylyphenylboronic acid with a 99% yield when activated with sodium bis(2-methoxyethoxy)aluminiumhydride, also on the kilogram scale.
[8] 4-Formylphenyl boronic acid crystallizes in colorless needles[1] or is obtained as an odorless, whitish powder, which dissolves little in cold but better in hot water.
The compound is quite stable[3] and readily forms dimers and cyclic trimeric anhydrides, which complicate purification and tend to protodeboronize, a secondary reaction that occurs frequently in the Suzuki coupling, with elimination of the boronic acid function.
[12] The addition of 4-FPBA in amounts < 0.08 wt% in the formulation reduces the loss of hydrolytic activity of the enzymes used and increases the storage stability of enzyme-containing liquid detergents.