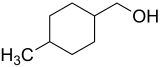
4-Methylcyclohexanemethanol
Both cis and trans isomers exist, depending on the relative positions of the methyl (CH3) and hydroxymethyl (CH2OH) groups on the cyclohexane ring.
[11] Eastman Chemical Company's MSDS for "crude" (unpurified) MCHM, as supplied by NPR, reports an oral LD-50 of 825 mg/kg and a dermal LD-50 greater than 2,000 mg/kg, both in rats.
The toxicity and environmental properties of these naphthenic acids have been well studied recently due to their occurrence as a major contaminant in water used for extraction of oil from tar sands.
[16] Cyclohexanemethanol (or cyclohexylmethanol, CHM, CAS 100–49–2), another closely related compound, which differs only in lacking a methyl substituent, has been found as a naturally occurring fusel alcohol in mango wine at concentrations of 1.45 mg/L, in which it is considered an aroma constituent.
Dermal application of "neat" (pure, undiluted) cis-p-menthan-7-ol at 2 g/kg bodyweight produced toxic effects in rats and rabbits.
[20] Another CHM derivative, 2,4-dimethylcyclohexanemethanol (CAS 68480–15–9, also dihydrofloralol or floral methanol), which has two methyl substituents instead of one, is frequently marketed as a fragrance or flavor additive.
One web site, Fantastic Flavours provides a list of recognized flavor additives for Japan, which includes 2,4-dimethylcyclohexanemethanol by virtue of being in the group of aliphatic higher alcohols.
[25] The external affairs manager of West Virginia American Water said that the spill originated with Freedom Industries, a Charleston company.