Abortion law in the United States by state
However, Roe and Casey were overturned by Dobbs v. Jackson Women's Health Organization (2022), and states may now impose any regulation on abortion, provided it satisfies rational basis review and does not otherwise conflict with federal law.
For comparative purposes, the youngest child thought to have survived a premature birth in the United States was Curtis Means born on July 5, 2020, in Birmingham, Alabama, at a gestational age of 21 weeks and one day.
Governor of Arizona Katie Hobbs and state Attorney General Kris Mayes are both supporters of abortion rights, elected in 2022 as part of a nationwide backlash to the Dobbs decision.
Nurse-midwives and other non-physician qualified medical personnel with proper training may perform abortion procedures early in pregnancy.
[43] On April 1, 2024, the Court approved Amendment 4, an initiative that appeared on the 2024 ballot that, if passed, would have allowed abortion up to the point of fetal viability.
Abortion is legal in Guam up to 13 weeks; up to 26 weeks in cases of rape, incest, or if "the child would be born with a grave physical or mental defect"; or at any time if a physician can demonstrate "substantial risk that continuance of the pregnancy would endanger the life of the mother, or would gravely impair the physical or mental health of the mother".
[69] Abortion is currently illegal in Indiana,[70] with exceptions for fatal fetal abnormalities, to preserve the life and physical health of the pregnant woman, or (before 10 weeks post-fertilization) in cases of rape or incest.
[71][72] Abortion in Iowa is illegal after 6 weeks of gestation,[73] with exceptions for rape, incest, fetal abnormalities, and the pregnant woman's life.
[75] Kansas lawmakers approved sweeping anti-abortion legislation (HB 2253) on April 6, 2013,[76] that says life begins at fertilization, forbids abortion based on "gender", and bans Planned Parenthood from providing sex education in schools.
[80] A proposed constitutional amendment that would have superseded this ruling was decisively rejected by voters on August 2, 2022,[81] six weeks after Roe was overturned in Dobbs v. Jackson Women's Health Organization.
A 2024 Montana Supreme Court decision established that minors do not need parental consent to have an abortion, overruling a state law.
[140] Nevada is the only state in the country that criminalizes a woman performing a self-managed abortion by "any drug, medicine, or substance, or any instrument or other means" after the 24th week of pregnancy.
[152] This expands the already existing Equal Protection Clause in the Constitution of New York which prohibits the denial of rights for a person based on "race, color, creed, or religion".
[158][159] The law technically made exceptions to save the life of the pregnant woman, or, until 6 weeks into a pregnancy, in cases of rape or incest.
[160] After the Supreme Court overturned Roe v. Wade on June 24, 2022, North Dakota moved to ban "almost all abortions, except in the case of rape, incest, or where the mother's life is at risk".
[172] On May 20, 2016, Governor Mary Fallin vetoed the bill before it could become law, citing its wording as too vague to withstand a legal challenge.
[175][176] HB 4327 is modeled after the Texas Heartbeat Act, and is enforced solely through civil lawsuits brought by private citizens, making it exceedingly difficult for abortion providers to challenge the constitutionality of the statute in court.
[177][178] On April 12, 2022, Governor Kevin Stitt signed into law SB 612,[171] a bill that banned abortion indefinitely, unless the life of the pregnant woman was at stake, with no exceptions to rape and incest.
[182] In 2024, the Pennsylvania Supreme Court ruled that the state's Medicaid program was required to pay for abortion services for participating residents.
[189] A 5-to-6-week abortion ban that had been passed before Dobbs as a trigger law was struck down in January 2023 by the South Carolina Supreme Court, which said it violated the state constitution.
[190] A newly passed 5-to-6-week ban went in effect in August 2023, after the justice who wrote the opinion in the original case retired; the new law was judged constitutional by the state supreme court.
Doctors are permitted to use their "reasonable medical judgement, based upon the facts known to the physician at the time", to determine if a situation falls into one of these exceptions.
[212][213] After the Supreme Court overturned Roe v. Wade on June 24, 2022, Texas completely banned abortions, except when the pregnant woman's life is at risk.
[216] The purpose of the lawsuit is to force the state to issue regulations clarifying the medical exception clause, rather than to overturn Texas's abortion ban entirely.
The laws' enforcement mechanism is based on civil lawsuits, like the Texas Heartbeat Act, making them difficult to challenge in court.
[227] Abortion is illegal in West Virginia,[228] except if necessary to preserve the life or health of a pregnant woman, if the fetus has a fatal anomaly, or if (up to 14 weeks) the pregnancy is the result of rape or incest.
An initial July 2023 ruling by a Dane County trial judge found that an 1849 law previously considered a trigger ban does not apply to consensual abortions performed by medical staff.
However, Wisconsin Attorney General Josh Kaul, a supporter of abortion rights, sued in state court to attempt to overturn the law; the Dane County ruling was the first in that case.
Abortions are offered by Planned Parenthood of Wisconsin in Milwaukee, Dane, and Sheboygan Counties, whose district attorneys have stated that they will not file charges based on the 1849 ban.
[243] In 2022, state legislation attempted to make abortion illegal, except in cases of rape, incest, or harm to the health of the pregnant woman, but enforcement was blocked by the courts, pending a final decision on the law's constitutionality.

|
Illegal, limited exceptions
[
a
]
Legal, but no providers
Legal through 12th week LMP*
Legal through 18th week LMP*
Legal through 22nd week LMP* (5 months)
Legal through 24th week LMP* (5½ months)
Legal through second trimester
[
d
]
Legal at any stage
*LMP is the time since the last menstrual period began.
|
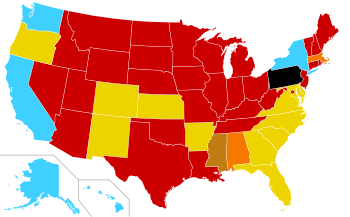

2 Illinois's parental notification law was repealed June 1, 2022.
3 Massachusetts' parental consent law only applies to minors under the age of 16. South Carolina's law only apples to minors under 17.





