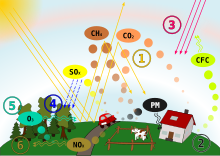
Acid rain
[3] In ecosystems, persistent acid rain reduces tree bark durability, leaving flora more susceptible to environmental stressors such as drought, heat/cold and pest infestation.
[4][5][6][7] Some governments, including those in Europe and North America, have made efforts since the 1970s to reduce the release of sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxide into the atmosphere through air pollution regulations.
Waldemar Christofer Brøgger was the first to acknowledge long-distance transportation of pollutants crossing borders from the United Kingdom to Norway – a problem systematically studied by Brynjulf Ottar in the 1970s.
[19] Ottar's work was strongly influenced[20] by Swedish soil scientist Svante Odén, who had drawn widespread attention to Europe's acid rain problem in popular newspapers and wrote a landmark paper on the subject in 1968.
[32] President Ronald Reagan dismissed the issues of acid rain[33] until his personal visit to Canada and confirmed that the Canadian border suffered from the drifting pollution from smokestacks originating in the US Midwest.
[40] Title IV of these amendments established a cap and trade system designed to control emissions of sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides.
[44] Forbes says: "In 2010, by which time the cap and trade system had been augmented by the George W. Bush administration's Clean Air Interstate Rule, SO2 emissions had fallen to 5.1 million tons.
The first recorded example of using the term is from 1989, describing how 225 volunteers across the US collected rain samples to assist the Audubon Society in an acid-rain awareness-raising campaign.
[53] This research showed both that acidification was linked to declining fish populations and that the effects could be reversed if sulfuric acid emissions decreased, and influenced policy in Canada and the United States.
[51] In 1985, seven Canadian provinces (all except British Columbia, Alberta, and Saskatchewan) and the federal government signed the Eastern Canada Acid Rain Program.
Acid rain has been a reported cause of decrease in soil pH, especially in the areas of northeast, coastal regions of Karnataka, Kerala, Odisha, Bihar, and West Bengal.
Nitric acid in rainwater is an important source of fixed nitrogen for plant life, and is also produced by electrical activity in the atmosphere such as lightning.
[63] The principal cause of acid rain is sulfur and nitrogen compounds from human sources, such as electricity generation, animal agriculture, factories, and motor vehicles.
[73] Both the lower pH and higher aluminium concentrations in surface water that occur as a result of acid rain can cause damage to fish and other aquatic animals.
Acid rain has eliminated insect life and some fish species, including the brook trout in some lakes, streams, and creeks in geographically sensitive areas, such as the Adirondack Mountains of the United States.
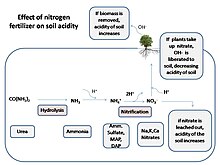
[5] Soil chemistry can be dramatically changed when base cations, such as calcium and magnesium, are leached by acid rain, thereby affecting sensitive species, such as sugar maple (Acer saccharum).
[88] Acid rain also has the ability to cause deformation to leaves at a cellular level, examples include; tissue scaring and changes to the stomatal, epidermis and mesophyll cells.
At higher altitudes, acidic fog and clouds can deplete nutrients from tree foliage, leading to discolored or dead leaves and needles.
[90] Other plants can also be damaged by acid rain, but the effect on food crops is minimized by the application of lime and fertilizers to replace lost nutrients.
In cultivated areas, limestone may also be added to increase the ability of the soil to keep the pH stable, but this tactic is largely unusable in the case of wilderness lands.
[91][92] Acid rain may also affect crop productivity by necrosis or changes to soil nutrients, which ultimately prevent plants from reaching maturity.
In addition to acidification, excess nitrogen inputs from the atmosphere promote increased growth of phytoplankton and other marine plants, which, in turn, may cause more frequent harmful algal blooms and eutrophication (the creation of oxygen-depleted "dead zones") in some parts of the ocean.
[97] A 25 parts per million (ppm) maximum for nitric oxide in working air has been set by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) for an 8-hour workday and a 40-hour workweek.
[98] The not-to-exceed limits in the air, water, soil, or food that are recommended by regulations are often based on levels that affect animals before being modified to assist in safeguarding people.
Depending on whether they employ different animal studies, have different exposure lengths (e.g., an 8-hour workday versus a 24-hour day), or for other reasons, these not-to-exceed values can vary between federal bodies.
Acid rain can damage buildings, historic monuments, and statues, especially those made of rocks, such as limestone and marble, that contain large amounts of calcium carbonate.
[105] The effectiveness of the Convention in combatting acid rain has inspired further acts of international commitment to prevent the proliferation of particulate matter.
Activity of the Long-Range Transboundary Air Pollution Convention remained dormant after 1999, when 27 countries convened to further reduce the effects of acid rain.
[108] In 2023, the EANET member countries include Cambodia, China, Indonesia, Japan, Lao PDR, Malaysia, Mongolia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Republic of Korea, Russia, Thailand and Vietnam.
To achieve this goal at the lowest cost to society, the program employs both regulatory and market based approaches for controlling air pollution.