Acupuncture
However, it can be divided into two main foundational philosophical applications and approaches; the first being the modern standardized form called eight principles TCM and the second being an older system that is based on the ancient Daoist wuxing, better known as the five elements or phases in the West.
[7][24][25] Acupuncture is believed to have originated around 100 BC in China, around the time The Inner Classic of Huang Di (Huangdi Neijing) was published,[26] though some experts suggest it could have been practiced earlier.
[13] For example, the American Society of Anesthesiologists states it may be considered in the treatment of nonspecific, noninflammatory low back pain only in conjunction with conventional therapy.
[2] Traditional acupuncture involves needle insertion, moxibustion, and cupping therapy,[17] and may be accompanied by other procedures such as feeling the pulse and other parts of the body and examining the tongue.
[43] Inquiring involves focusing on the "seven inquiries": chills and fever; perspiration; appetite, thirst and taste; defecation and urination; pain; sleep; and menses and leukorrhea.
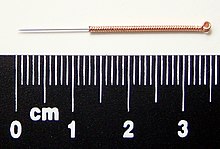
[47] Japanese acupuncturists use extremely thin needles that are used superficially, sometimes without penetrating the skin, and surrounded by a guide tube (a 17th-century invention adopted in China and the West).
[49] De-qi (Chinese: 得气; pinyin: dé qì; "arrival of qi") refers to a claimed sensation of numbness, distension, or electrical tingling at the needling site.
[36] As of 2021[update], many thousands of papers had been published on the efficacy of acupuncture for the treatment of various adult health conditions, but there was no robust evidence it was beneficial for anything, except shoulder pain and fibromyalgia.
[78] However, some physicians and ethicists have suggested circumstances for applicable uses for placebos such as it might present a theoretical advantage of an inexpensive treatment without adverse reactions or interactions with drugs or other medications.
[11] These included Australia, Austria, Canada, Croatia, France, Germany, Ireland, the Netherlands, New Zealand, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, the UK, and the US.
[19] Although acupuncture is generally considered a safe procedure, a 2013 review stated that the reports of infection transmission increased significantly in the prior decade, including those of mycobacterium.
[92] The same review concluded that cardiac tamponade was a serious, usually fatal, though theoretically avoidable complication following acupuncture, and urged training to minimize risk.
[92] A 2012 review found that a number of adverse events were reported after acupuncture in the UK's National Health Service (NHS), 95% of which were not severe,[40] though miscategorization and under-reporting may alter the total figures.
[94] A causal link between acupuncture and the adverse events cardiac arrest, pyknolepsy, shock, fever, cough, thirst, aphonia, leg numbness, and sexual dysfunction remains uncertain.
[2] Four adverse events associated with moxibustion were bruising, burns and cellulitis, spinal epidural abscess, and large superficial basal cell carcinoma.
[17] The minor ones were keloid scarring, burns, and bullae;[17] the serious ones were acquired hemophilia A, stroke following cupping on the back and neck, factitious panniculitis, reversible cardiac hypertrophy, and iron deficiency anemia.
"[101] Stephen Barrett states that there is a "risk that an acupuncturist whose approach to diagnosis is not based on scientific concepts will fail to diagnose a dangerous condition".
[105] In TCM, disease is generally perceived as a disharmony or imbalance in energies such as yin, yang, qi, xuĕ, zàng-fǔ, meridians, and of the interaction between the body and the environment.
[120] Some modern practitioners support the use of acupuncture to treat pain, but have abandoned the use of qi, meridians, yin, yang and other mystical energies as an explanatory frameworks.
[26] Gold and silver needles found in the tomb of Liu Sheng from around 100 BC are believed to be the earliest archaeological evidence of acupuncture, though it is unclear if that was their purpose.
[29] This has been cited as evidence that practices similar to acupuncture may have been practised elsewhere in Eurasia during the early Bronze Age;[126] however, The Oxford Handbook of the History of Medicine calls this theory "speculative".
[28]: 74 Lu and Needham noted that all the ancient materials that could have been used for acupuncture and which often produce archaeological evidence, such as sharpened bones, bamboo or stones, were also used for other purposes.
Over time, the focus shifted from blood to the concept of puncturing specific points on the body, and eventually to balancing Yin and Yang energies as well.
[124] Ramey and Buell said the "practice and theoretical underpinnings" of modern acupuncture were introduced in The Yellow Emperor's Classic (Huangdi Neijing) around 100 BC.
[28]: 101 In the first half of the 1st century AD, acupuncturists began promoting the belief that acupuncture's effectiveness was influenced by the time of day or night, the lunar cycle, and the season.
[26] Western practitioners abandoned acupuncture's traditional beliefs in spiritual energy, pulse diagnosis, and the cycles of the moon, sun or the body's rhythm.
The US Congress created the Office of Alternative Medicine in 1992 and the National Institutes of Health (NIH) declared support for acupuncture for some conditions in November 1997.
[149] CDC clinical practice guidelines from 2022 list acupuncture among the types of complementary and alternative medicines physicians should consider in preference to opioid prescription for certain kinds of pain.
[151] As a result of the trials, German public health insurers began to cover acupuncture for chronic low back pain and osteoarthritis of the knee, but not tension headache or migraine.
This inclusion granted qualified and professionally registered acupuncturists the ability to provide subsidised care and treatment to citizens, residents, and temporary visitors for work- or sports-related injuries that occurred within the country of New Zealand.