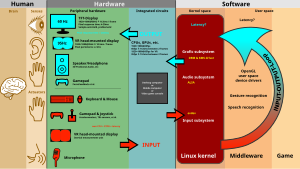
Advanced Linux Sound Architecture
Some of the goals of the ALSA project at its inception were automatic configuration of sound-card hardware and graceful handling of multiple sound devices in a system.
The project to develop ALSA was led by Jaroslav Kysela, and was based on the Linux device driver for the Gravis Ultrasound sound card.
While ALSA may be configured to provide an OSS emulation layer, such functionality is no longer available or is not installed by default in many Linux distributions.
Additional to the software framework internal to the Linux kernel, the ALSA project also provides the command-line tools[8][9][10] and utilities[11] alsactl,[12] amixer,[13] arecord/aplay and alsamixer,[13] an ncurses-based TUI.
There also are GUIs programmed by third-party developers, such as GNOME-ALSAmixer[14] (using GTK), Kmix,[14] XFCE4-mixer, LXpanel, QasHctl, QasMixer, Pavucontrol, AconnectGUI,[15] tapiir,[15] polarbear,[15] ALSAmixerGUI[16] (using FLTK), ZynAddSubFX, Yoshimi, and even more.
The hw interface provides direct access to the kernel device, but no software mixing or stream adaptation support.