Aerodynamic force
There are two causes of aerodynamic force: [1]: §4.10 [2][3]: 29 Pressure acts normal to the surface, and shear force acts parallel to the surface.
The net aerodynamic force on the body is equal to the pressure and shear forces integrated over the body's total exposed area.
[4] When an airfoil moves relative to the air, it generates an aerodynamic force determined by the velocity of relative motion, and the angle of attack.
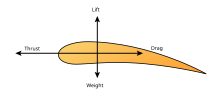
This aerodynamic force is commonly resolved into two components, both acting through the center of pressure:[3]: 14 [1]: § 5.3 In addition to these two forces, the body may experience an aerodynamic moment.
The aerodynamic force on a powered airplane is commonly represented by three vectors: thrust, lift and drag.