Amavadin
Amavadin is a vanadium-containing anion found in three species of poisonous Amanita mushrooms: A. muscaria, A. regalis, and A.
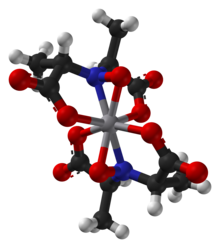
[1] A Ca2+ cation is often used to crystallize amavadin to obtain a good quality X-ray diffraction.
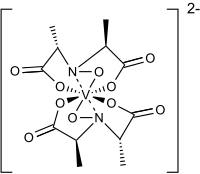
In 1993, it was discovered by crystallographic characterization that amavadin is not a vanadyl ion compound.
The anion features five chiral centers, one at vanadium and the four carbon atoms having S stereochemistry.
The biological function of amavadin is still unknown, yet it has been thought that it uses H2O2 and acts as a peroxidase to aid the regeneration of damaged tissues.