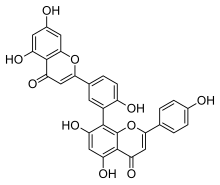
Amentoflavone
Amentoflavone is a biflavonoid (bis-apigenin coupled at 8 and 3′ positions, or 3′,8″-biapigenin) constituent of a number of plants including Ginkgo biloba, Chamaecyparis obtusa (hinoki), Biophytum sensitivum, Selaginella tamariscina,[1] Hypericum perforatum (St. John's Wort)[2] and Xerophyta plicata.
[3] Amentoflavone can interact with many medications by being a potent inhibitor of CYP3A4 and CYP2C9, which are enzymes responsible for the metabolism of some drugs in the body.
[4] It is also an inhibitor of human cathepsin B.
[2] Amentoflavone has a variety of in vitro activities including antimalarial activity,[5] anticancer activity (which may, at least in part, be mediated by its inhibition of fatty acid synthase),[6][7][8] and antagonist activity at the κ-opioid receptor (Ke = 490 nmol L−1)[9] as well as activity at the allosteric benzodiazepine site of the GABAA receptor as a negative allosteric modulator.
[10]