Education in the United States
According to a 2018 study in the Economic Journal, states were more likely to adopt compulsory education laws during the Age of Mass Migration (1850–1914) if they hosted more European immigrants with lower exposure to civic values.
Gradually by the late 1890s, regional associations of high schools, colleges and universities were being organized to coordinate proper accrediting standards, examinations, and regular surveys of various institutions in order to assure equal treatment in graduation and admissions requirements, as well as course completion and transfer procedures.
In terms of sponsoring innovation; however, then-President Obama and then-Education Secretary Arne Duncan pursued K-12 education reform through the Race to the Top grant program.
In the competition, points were awarded for allowing charter schools to multiply, for compensating teachers on a merit basis including student test scores, and for adopting higher educational standards.
Complaints also came from middle-class families, who were annoyed at the increasing emphasis on teaching to the test, rather than encouraging teachers to show creativity and stimulating students' imagination.
[55][56][57][58][59] Like every wealthy country, the COVID-19 pandemic and Deltacron hybrid variant had a great impact on education in the United States, requiring schools to implement technology and transition to virtual meetings.
[4] Summer 2022 polls and surveys revealed that mental health issues were reported by 60% of college students, with educational institutions being understaffed and unprepared to effectively address the crisis.
It involved lengthy interviews of over 26,700 adults statistically balanced for age, gender, ethnicity, education level, and location (urban, suburban, or rural) in 12 states across the U.S. and was designed to represent the U.S. population as a whole.
"[105] Federal legislation proposed in December 2022 and endorsed February 2023 by Senate Finance Committee chair Bernie Sanders would set a minimum salary of $60,000 per year for teachers.
[citation needed] Many graduate students do not start professional schools immediately after finishing undergraduate studies but work for a time while saving up money or deciding on a career direction.
[119] There are over 7,000 post-secondary institutions in the United States offering a diverse number of programs catered to students with different aptitudes, skills, and educational needs.
Common admission requirements to gain entry to any American university requires a meeting a certain age threshold, high school transcript documenting grades, coursework, and rigor of core high school subject areas as well as performance in AP and IB courses, class ranking, ACT or SAT scores, extracurricular activities, an admissions essay, and letters of recommendation from teachers and guidance counselors.
[121] These rankings are based on factors such as brand recognition, number of Nobel Prize winners, selectivity in admissions, generosity of alumni donors, and volume and quality of faculty research.
Community and junior colleges in the United States are public comprehensive institutions that offer a wide range of educational services that generally lasts two years.
Though it is cheaper in terms of tuition, less competitive to get into, and not as prestigious as going to a four-year university, they form another post-secondary option for students seeking to enter the realm of American higher education.
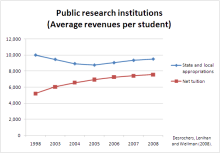
In response to this phenomenon, California's citizens passed Proposition 13 in 1978, which severely restricted the ability of the Legislature to expand the state's educational system to keep up with growth.
The other half is managed by commercial entities such as banks, credit unions, and financial services firms such as Sallie Mae, under the Federal Family Education Loan Program (FFELP).
[167] In 2006, A survey reported by Reader's Digest found that 50% to 95% of American students admitted to having cheated in high school or college at one time or another, results that cast some doubt on measured academic attainment tests.
[174][175][176] A major criticism of American educational curricula is that it overemphasizes math and reading skills without providing the content knowledge needed to understand the texts used to teach the latter.
[177] Reading skills are typically taught using a three cues system based on identifying meaning, sentence structure, and visual information such as the first letter in a word.
[178][179] This method has been criticized by psychologists such as Timothy Shanahan for lacking a basis in scientific evidence, citing studies that find that good readers look at all the letters in a word.
[188] According to a 1997 report by the U.S. Department of Education, passing rigorous high-school mathematics courses predicts successful completion of university programs regardless of major or family income.
[194] A 1999 study by the Guttmacher Institute found that most U.S. sex education courses in grades 7 through 12 cover puberty, HIV, STDs, abstinence, implications of teenage pregnancy, and how to resist peer pressure.
[197] At least 20 states have had their legislatures introduce derivative bills of the Florida Parental Rights in Education Act, including Arizona,[198] Georgia,[199] Iowa,[200][201] Kentucky, Louisiana, Michigan,[202] Missouri,[203] Ohio,[204] Oklahoma,[205] Tennessee, and South Carolina.
[210] In 2010, the Texas Board of Education passed more than 100 amendments to the curriculum standards, affecting history, sociology, and economics courses to 'add balance' given that academia was 'skewed too far to the left'.
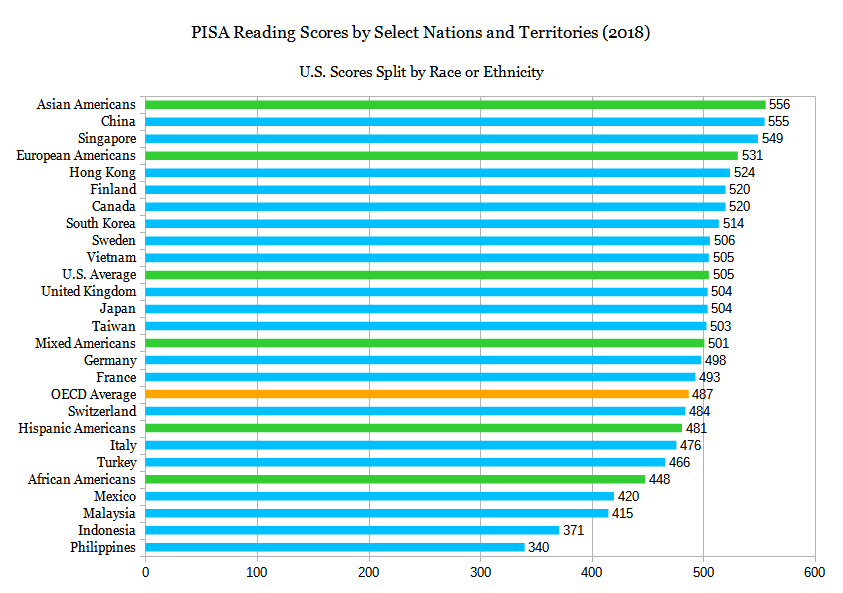
[225][226][227][228][229] Other explanations offered for the racial achievement gap include: social class, institutional racism, lower quality of schools and teachers in minority communities, and civil injustice.
In an economic analysis, consulting firm McKinsey & Company reports that closing the educational achievement gap between the United States and nations such as Finland and Korea would have increased US GDP by 9–16% in 2008.
[234] The United States has fallen behind the rest of the developed world in education, creating a global achievement gap that alone costs the nation 9–16% of potential GDP each year.
[235] The school-to-prison pipeline (SPP) is the disproportionate tendency of minors and young adults from disadvantaged backgrounds to become incarcerated, because of increasingly harsh school and municipal policies which mirror law enforcement methods.
[245] Teachers believe that parents are not supervising their children's free time to encourage the learning process, such as basic literacy, which is crucial not only to later success in life but also to keep them out of prison.