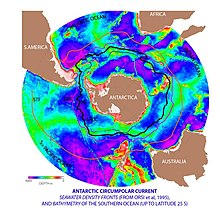
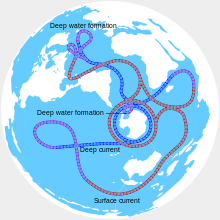
Antarctic Circumpolar Current
These nurture high levels of phytoplankton with associated copepods and krill, and resultant food chains supporting fish, whales, seals, penguins, albatrosses, and a wealth of other species.
Jack London's story "Make Westing" and the circumstances preceding the mutiny on the Bounty poignantly illustrate the difficulty it caused for mariners seeking to round Cape Horn westbound on the clipper ship route from New York to California.
To trace it starting arbitrarily at South America, it flows through the Drake Passage between South America and the Antarctic Peninsula and then is split by the Scotia Arc to the east, with a shallow warm branch flowing to the north in the Falkland Current and a deeper branch passing through the Arc more to the east before also turning to the north.
Much of the ACC transport is carried in this front, which is defined as the latitude at which a subsurface salinity minimum or a thick layer of unstratified Subantarctic mode water first appears, allowed by temperature dominating density stratification.
There is a relatively small addition of flow in the Indian Ocean, with the transport south of Tasmania reaching around 147 Sv, at which point the current is probably the largest on the planet.
The increasing eastward momentum imparted by the winds causes water parcels to drift outward from the axis of the Earth's rotation (in other words, northward) as a result of the Coriolis force.
This northward Ekman transport is balanced by a southward, pressure-driven flow below the depths of the major ridge systems.
Such theories link the magnitude of the Circumpolar Current with the global thermohaline circulation, particularly the properties of the North Atlantic.
Trends in the Antarctic Oscillation have been hypothesized to account for an increase in the transport of the Circumpolar Current over the past two decades.
Published estimates of the onset of the Antarctic Circumpolar Current vary, but it is commonly considered to have started at the Eocene/Oligocene boundary.
The Tasmanian Seaway separates East Antarctica and Australia, and is reported to have opened to water circulation 33.5 million years ago (Ma).
Diatom production continues through the summer, and populations of krill are sustained, bringing large numbers of cetaceans, cephalopods, seals, birds, and fish to the area.
[13] Phytoplankton blooms are believed to be limited by irradiance in the austral (southern hemisphere) spring, and by biologically available iron in the summer.
[17] An expedition in May 2008 by 19 scientists[18] studied the geology and biology of eight Macquarie Ridge sea mounts, as well as the Antarctic Circumpolar Current to investigate the effects of climate change of the Southern Ocean.
[6] After studying the circumpolar current it is clear that it strongly influences regional and global climate as well as underwater biodiversity.
[22] UNESCO mentions that the report in the first time "notes a growing scientific consensus that melting Greenland and Antarctic ice sheets, among other factors, may be slowing important ocean currents at both poles, with potentially dire consequences for a much colder northern Europe and greater sea-level rise along the U.S. East Coast.