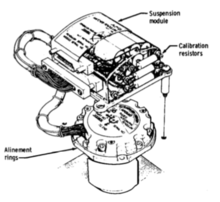
Apollo PGNCS
The Apollo primary guidance, navigation, and control system (PGNCS, pronounced pings) was a self-contained inertial guidance system that allowed Apollo spacecraft to carry out their missions when communications with Earth were interrupted, either as expected, when the spacecraft were behind the Moon, or in case of a communications failure.
The prime contractor for PGNCS and manufacturer of the inertial measurement unit (IMU) was the Delco Division of General Motors.
However high humidity conditions inside the crew compartments and accidents in handling body fluids during the Gemini 7 mission made having unsealed electrical connections undesirable.
The CM optical unit had a precision sextant (SXT) fixed to the IMU frame that could measure angles between stars and Earth or Moon landmarks or the horizon.
The optical unit also included a low-magnification wide field of view (60°) scanning telescope (SCT) for star sightings.
The outer element of the AOT was a sun-shielded prism that could be rotated to one of six fixed positions relative to the LM, in order to cover a large portion of the lunar sky.
When rotated, the AOT's position was readable by the AGC; by pointing the reticule at two different stars, the computer could determine the craft's orientation.
[2] Apollo 11 Command Module Pilot Michael Collins noted that the visibility through the optics was sub-standard, and it was difficult to see through in certain lighting conditions.
Tracking data from NASA's Deep Space Network was processed by computers at Mission Control, using least squares algorithms.
PGNCS was still essential to maintain spacecraft orientation, to control rockets during maneuvering burns, including lunar landing and take off, and as the prime source of navigation data during planned and unexpected communications outages.
During Apollo 13, after the most critical burn near the Moon, the AGS was used in place of PGNCS because it required less electrical power and cooling water.