Archegonium
: archegonia), from the Ancient Greek ἀρχή ("beginning") and γόνος ("offspring"), is a multicellular structure or organ of the gametophyte phase of certain plants, producing and containing the ovum or female gamete.
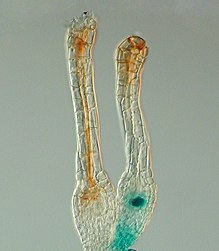
[citation needed] In the moss Physcomitrella patens, archegonia are not embedded but are located on top of the leafy gametophore (s. Figure).
The Polycomb protein FIE is expressed in the unfertilized egg cell (right) as the blue colour after GUS staining reveals.
Soon after fertilisation, the FIE gene is inactivated (the blue colour is no longer visible, left) in the young embryo.
The function of surrounding the gamete is assumed in large part by diploid cells of the megasporangium (nucellus) inside the ovule.