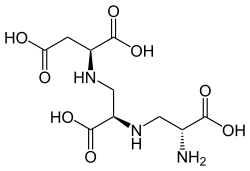
Aspergillomarasmine A
[1] Aspergillomarasmine A is toxic to leaves of barley and other plants, being termed as "Toxin C" when produced by Pyrenophora teres.
[3] In addition to Aspergillus versicolor, aspergillomarasmine A is also produced by the ascomycete Pyrenophora teres where it acts as a toxin in the barley net-spot blotch disease.
In P. teres, a biosynthetic precursor of aspergillomarasmine A, L,L-N-(2-amino-2-carboxyethyl)-aspartic acid has also been isolated and found to contribute to the phytotoxic properties of this microbe.
The chemical is insoluble in common organic solvents, but can dissolve in water under either basic or strongly acidic conditions.
[7] It can inhibit endothelin converting enzymes even in the live rat, probably by chelating metals required by metalloproteases.