Astronomical nutation
This is important because the most commonly used frame of reference for measurement of the positions of astronomical objects is the Earth's equator — the so-called equatorial coordinate system.
It is then necessary to apply a further correction to take into account the effect of nutation, after which the position relative to the true equinox and equator is obtained.
There is another disturbance of the Earth's rotation called polar motion that can be estimated for only a few months into the future because it is influenced by rapidly and unpredictably varying things such as ocean currents, wind systems, and hypothesised motions in the liquid nickel-iron outer core of the Earth.
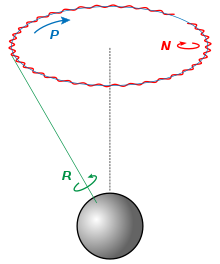
Precession and nutation are caused principally by the gravitational forces of the Moon and Sun acting upon the non-spherical figure of the Earth.
Precession is the effect of these forces averaged over a very long period of time, and a time-varying moment of inertia (If an object is asymmetric about its principal axis of rotation, the moment of inertia with respect to each coordinate direction will change with time, while preserving angular momentum), and has a timescale of about 26,000 years.
The largest contributor to nutation is the inclination of the orbit of the Moon around the Earth, at slightly over 5° to the plane of the ecliptic.
) can be calculated approximately as follows:[3] Earth also has an additional 0.10 to 0.15 seconds of arc nutations with a period 6 and half years called Chandler wobble and its due to free nutation caused by irregular distribution of mass around Earth axis.
These observations were originally intended to demonstrate conclusively the existence of the annual aberration of light, a phenomenon that Bradley had unexpectedly discovered in 1725-6.
However, there were some residual discrepancies in the stars' positions that were not explained by aberration, and Bradley suspected that they were caused by nutation taking place over the 18.6 year period of the revolution of the nodes of the Moon's orbit.
This was confirmed by his 20-year series of observations, in which he discovered that the celestial pole moved in a slightly flattened ellipse of 18 by 16 arcseconds about its mean position.
[5] Although Bradley's observations proved the existence of nutation and he intuitively understood that it was caused by the action of the Moon on the rotating Earth, it was left to later mathematicians, Jean le Rond d'Alembert and Leonhard Euler, to develop a more detailed theoretical explanation of the phenomenon.