Automatic train operation
[3] On most systems for lower grades of automation up to GoA2, there is a driver present to mitigate risks associated with failures or emergencies.
The combined system will marginally adjust operating parameters such as the ratio of power to coasting when moving and station dwell time in order to adhere to a defined timetable.
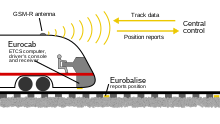
[citation needed] Whereas ATP is the safety system that ensures a safe spacing between trains and provides sufficient warning as to when to stop.
When it reaches the first beacon – originally a looped cable, now usually a fixed transponder – a station brake command is received by the train.
[20] In 2021, the Florida Department of Transportation funded a review by scientists from Florida State University, University of Talca and Hong Kong Polytechnic University, which showed the following advantages of autonomous trains:[21] While ATO has been proven to drastically reduce the chance of human errors in railway operation, there have been a few notable accidents involving ATO systems: 2.47 million €[43] 1.7 million €[47] In October 2021, the pilot project of the "world's first automated, driverless train" on regular tracks shared with other rail traffic was launched in Hamburg, Germany.
The conventional, standard-track, non-metro train technology could, according to reports, theoretically be implemented for rail transport worldwide and is also substantially more energy efficient.
Trains on the central London section of Thameslink were the first to use ATO on the UK mainline railway network[54] with ETCS Level 2.
In 2025, regular driverless passenger services on the line from Kopidlno to Dolní Bousov will be resumed by AŽD Praha.