Axonal transport
Motor proteins bind and transport several different cargoes including mitochondria, cytoskeletal polymers, autophagosomes, and synaptic vesicles containing neurotransmitters.
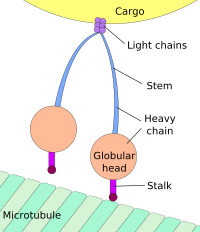
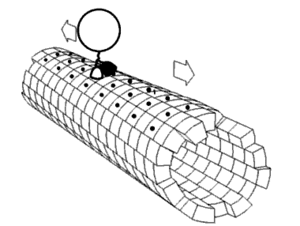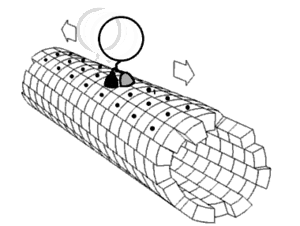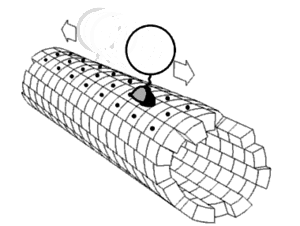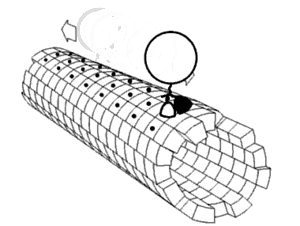
The anterograde movement of individual cargoes (in transport vesicles) of both fast and slow components along the microtubule[4] is mediated by kinesins.
During reactivation from latency, the herpes simplex virus (HSV) enters its lytic cycle, and uses anterograde transport mechanisms to migrate from dorsal root ganglia neurons to the skin or mucosa that it subsequently affects.
[14] A 15-amino acid peptide in the cytoplasmic carboxyl terminus of APP binds with high affinity to conventional kinesin-1 and mediates transport of exogenous cargo in the giant axon of the squid.
[16] Transport from hippocampus to forebrain is decreased in aging and destination is altered by the presence of Alzheimer's disease plaques.
Retrograde transport carries survival signals from the synapse back to the cell body, such as the TRK, the nerve growth factor receptor.
[21] Herpes simplex virus travels both ways in axons depending on its life cycle, with retrograde transport dominating polarity for incoming capsids.
Several rare neurodegenerative diseases are linked to genetic mutations in the motor proteins, kinesin and dynein, and in those cases, it is likely that axonal transport is a key player in mediating pathology.
Arrest of axoplasmic flow at the edge of ischemic areas in vascular retinopathies leads to swelling of nerve fibres, which give rise to soft exudates or cotton-wool patches.
[25] The tetanus neurotoxin is internalised at the neuromuscular junction through binding the nidogen proteins and is retrogradely transported towards the soma in signaling endosomes.
[26] Neurotropic viruses, such as the herpesviruses, travel inside axons using cellular transport machinery, as has been shown in work by Elaine Bearer's group.