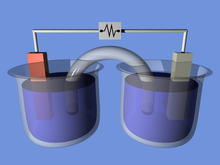
Electrochemical cell
[2] Both galvanic and electrolytic cells can be thought of as having two half-cells: consisting of separate oxidation and reduction reactions.
[4] A salt bridge or porous membrane connects the two solutions, keeping electric neutrality and the avoidance of charge accumulation.
An alternative to a salt bridge is to allow direct contact (and mixing) between the two half-cells, for example in simple electrolysis of water.
[citation needed] As electrons flow from one half-cell to the other through an external circuit, a difference in charge is established.
A salt bridge allows the flow of negative or positive ions to maintain a steady-state charge distribution between the oxidation and reduction vessels, while keeping the contents otherwise separate.
[1] Likewise, in the reduction reaction, the closer the equilibrium lies to the ion/atom with the more negative oxidation state the higher the potential.
)[citation needed] Important examples of electrolysis are the decomposition of water into hydrogen and oxygen, and of bauxite into aluminium and other chemicals.
[citation needed] The components of an electrolytic cell are:[citation needed] When driven by an external voltage (potential difference) applied to the electrodes, the ions in the electrolyte are attracted to the electrode with the opposite potential, where charge-transferring (also called faradaic or redox) reactions can take place.
Only with a sufficient external voltage can an electrolytic cell decompose a normally stable, or inert chemical compound in the solution.
[citation needed] Primary cells are made in a range of standard sizes to power small household appliances such as flashlights and portable radios.
Due to the toxic heavy metals and strong acids or alkalis they contain, batteries are hazardous waste.
It is a convenient way to store electricity: when current flows one way, the levels of one or more chemicals build up (charging); while it is discharging, they reduce and the resulting electromotive force can do work.
[11] They are used for primary and backup power for commercial, industrial and residential buildings and in remote or inaccessible areas.
They are also used to power fuel cell vehicles, including forklifts, automobiles, buses, boats, motorcycles and submarines.
[citation needed] In 2022, the global fuel cell market was estimated to be $6.3 billion, and is expected to increase by 19.9% by 2030.