Beam divergence
However, it is also used in the radio frequency (RF) band for cases in which the antenna is very large relative to a wavelength.
A beam may, for example, have an elliptical cross section, in which case the orientation of the beam divergence must be specified, for example with respect to the major or minor axis of the elliptical cross section.
of the beam in the rear focal plane of the lens is related to the divergence of the initial beam by where f is the focal length of the lens.
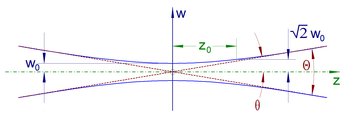
Like all electromagnetic beams, lasers are subject to divergence, which is measured in milliradians (mrad) or degrees.
For example, an ultraviolet laser that emits at a wavelength of 308 nm will have a lower divergence than an infrared laser at 808 nm, if both have the same minimum beam diameter.
This type of beam divergence is observed from optimized laser cavities.
Information on the diffraction-limited divergence of a coherent beam is inherently given by the N-slit interferometric equation.