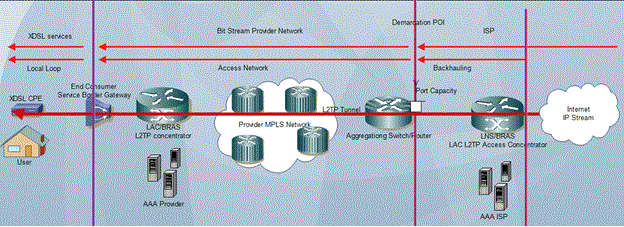
Bit-stream access
[1] The incumbent may also provide transmission services to its competitors, using its Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) or IP network, to carry competitors' traffic from the digital subscriber line access multiplexer (DSLAM) to a higher level in the network hierarchy where new entrants may already have a point of presence (e.g. a transit switch location).
It enables competitors to offer their own products to consumers even if they do not operate the local loop (the last mile).
Bit-stream access allows the new entrant to use the high-speed modems and other equipment provided by the incumbent and thus avoid maintenance and investments into the local loop.
This affects the economics of the service and places restrictions on the type of modems that the customer of the new entrant can buy or rent.
From the regulatory point of view, such services are therefore seen as complementing the other forms of unbundled access, but not substituting them.