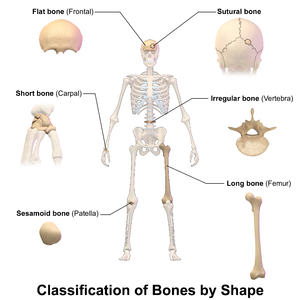
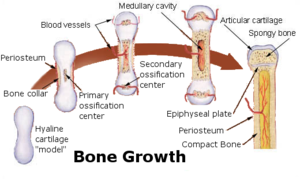
Bone
[23] The osteoid seam is a narrow region of a newly formed organic matrix, not yet mineralized, located on the surface of a bone.
[21] Osteoclasts are large cells with multiple nuclei located on bone surfaces in what are called Howship's lacunae (or resorption pits).
[29] The exact composition of the matrix may be subject to change over time due to nutrition and biomineralization, with the ratio of calcium to phosphate varying between 1.3 and 2.0 (per weight), and trace minerals such as magnesium, sodium, potassium and carbonate also be found.
Collagen consists of strands of repeating units, which give bone tensile strength, and are arranged in an overlapping fashion that prevents shear stress.
In cross-section, the fibers run in opposite directions in alternating layers, much like in plywood, assisting in the bone's ability to resist torsion forces.
Around and inside collagen fibrils calcium and phosphate eventually precipitate within days to weeks becoming then fully mineralized bone with an overall carbonate substituted hydroxyapatite inorganic phase.
[48] While nutritional and pharmacological approaches may also improve bone health, the strength and balance adaptations from resistance training are a substantial added benefit.
High-impact sports, which involve quick changes in direction, jumping, and running, are particularly effective with stimulating bone growth in the youth.
[49] Engaging in physical activity during childhood years, particularly in these high-impact osteogenic sports, can help to positively influence bone mineral density in adulthood.
[50] Children and adolescents who participate in regular physical activity will place the groundwork for bone health later in life, reducing the risk of bone-related conditions such as osteoporosis.
Influencing factors that can help us have larger stores and higher amounts of BMD will allow us to see less harmful results as we reach older adulthood.
[68] Another research study goes on to show that long-term calcium intake has been proven to significantly contribute to overall BMD in children without certain conditions or disorders.
[69] This data shows that ensuring adequate calcium intake in children reinforces the structure and rate at which bones will begin to densify.
In a recent study,[68] there was a strong correlation between calcium intake and BMD across a variety of diverse populations of children and adolescence ultimately coming to the conclusion that fundamentally, achieving optimal bone health is necessary for providing our youth with the ability to undergo hormonal changes as well.
They found in a study of over 10,000 children ages 8–19 that in females, African Americans, and the 12-15 adolescent groups that at 2.6-2.8g/kg of body weight, they began to see a decrease in BMD.
Being able to reach our daily value of 1300 mg for ages 9–18 [67] is becoming more and more necessary and as we progress in health, the chance that osteoporosis and other factors such as bone fragility or potential for stunted growth can be greatly reduced through these resources, ultimately leading to a more fulfilling and healthier lifestyle.
[70] The purpose of remodeling is to regulate calcium homeostasis, repair microdamaged bones from everyday stress, and to shape the skeleton during growth.
[75] Osteoblasts can also be induced to secrete a number of cytokines that promote reabsorption of bone by stimulating osteoclast activity and differentiation from progenitor cells.
[79] When serious, depending on the fractures type and location, complications may include flail chest, compartment syndromes or fat embolism.
This may lead to compression of the spinal cord, destruction of the marrow resulting in bruising, bleeding and immunosuppression, and is one cause of bone pain.
[83] Palliative care, which focuses on maximising a person's quality of life, may play a role in management, particularly if the likelihood of survival within five years is poor.
The weakening of these developmental aspects is thought to lead to an increased risk of developing many diseases such as osteoarthritis, osteoporosis, osteopenia and fractures.
[87] Development of any of these diseases is thought to be correlated with a decrease in ability to perform in athletic environments and activities of daily living.
Focusing on therapies that target molecules like osteocalcin or AGEs could provide new ways to improve bone health and help manage the complications of diabetes more effectively.
This density is measured using dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA), with the term "established osteoporosis" including the presence of a fragility fracture.
[97] Osteoporosis treatment includes advice to stop smoking, decrease alcohol consumption, exercise regularly, and have a healthy diet.
Calcium and trace mineral supplements may also be advised, as may Vitamin D. When medication is used, it may include bisphosphonates, Strontium ranelate, and hormone replacement therapy.
[100] One study done on children with developmental coordination disorder found an increase in bone mass up to 4% and 5% in the cortical areas of the tibia alone from a 13-week training period,[101] which is truly significant when considering how participants only participated in the multimodal workouts twice per week, and it would be reasonable to expect these increases to be greater if workouts were more frequent, especially in youth without developmental coordination disorder.
Some bones, primarily formed separately in subcutaneous tissues, include headgears (such as bony core of horns, antlers, ossicones), osteoderm, and os penis/os clitoris.
[115] They have further been used in bone carving, already important in prehistoric art, and also in modern time as crafting materials for buttons, beads, handles, bobbins, calculation aids, head nuts, dice, poker chips, pick-up sticks, arrows, scrimshaw, ornaments, etc.