Geography of Serbia
It shares borders with Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Hungary, North Macedonia, Montenegro, and Romania.
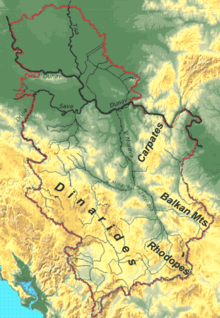
The terrain of central Serbia consists chiefly of hills and low to medium-high mountains, interspersed with numerous rivers and creeks.
The main communication and development line stretches southeast of Belgrade towards Niš and Skopje (in North Macedonia), along the valley formed by the Great and South Morava rivers.
To the east of this line, in an area that is relatively sparsely populated, the terrain rises to the limestone ranges of Stara Planina and the Serbian Carpathians.
[citation needed] Four mountain systems meet in Serbia: the Dinaric Alps in the west cover the greatest territory, stretching from northwest to southeast.
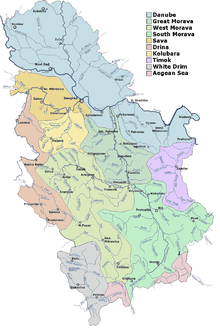
Practically the entire territory (92%) of Serbia belongs to the Danube (Black Sea) drainage basin.
The Danube flows 588 km through Serbia or as a border river (with Croatia in the northwest and Romania in the southeast).
The remainder could be generated in small and medium power plants (<25 MW), whose construction by the private sector may improve Serbia's economy and energy reliability.
Geothermal water is primarily used for balneological purposes: there are around 60 spas in Serbia, which are seen as an opportunity to improve tourism in the country.
[5] Climate of Serbia is moderate continental with a diversity on local level, caused by geographic location, relief, terrain exposition, presence of river and lake systems, vegetation, urbanization etc.
Proximity of the mountain ranges of Alps, Carpathians, Rhodopes, as well as Adriatic Sea and Pannonian plain affect the climate.