Bornaviridae
Horses, sheep, cattle, rodents, birds, reptiles, and humans serve as natural hosts.
The ICTV proposed the creation in 1996 of the family Bornaviridae along with the genus Bornavirus (today Orthobornavirus).
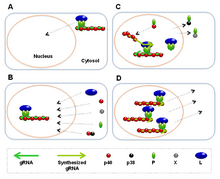
[2] Proteins of orthobornaviruses that have been characterized: In the Mononegavirales order, Bornaviridae is one of only two families with viruses that replicate in the nucleus.
Genomic analysis found a previously unknown orthobornavirus in a contact squirrel and in brain tissue from the three men, the researchers reported, and it is the "likely causative agent" in their deaths.
[10] Since behavioral disease has been studied in BoDV-1 infected animals like rhesus monkeys, tree shrews, and rats, BoDV-1 has also been hypothesized to be associated with humans psychiatric conditions such as schizophrenia and affective psychoses.