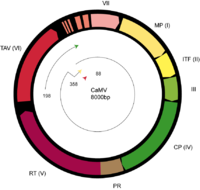
Caulimoviridae
This family contains all plant viruses with a dsDNA genome that have a reverse transcribing phase in their lifecycle.
The type of nucleocapsid incorporated into the virus structure determines the size of the viral particles.
The presence of endogenous viral elements (EVEs) in plant genomes is widespread.
[4][5][6] and most known plant EVEs originate from viruses with DNA genomes in the family Caulimoviridae.
Integration is thought to occur through non-homologous end-joining (illegitimate recombination) during DNA repair mechanisms.