Bubo
A bubo (Greek βουβών, boubṓn, 'groin') is adenitis or inflammation of the lymph nodes and is an example of reactive infectious lymphadenopathy.
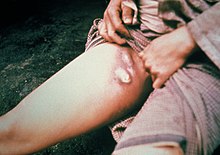
[1] Buboes are a symptom of bubonic plague and occur as painful swellings in the thighs, neck, groin or armpits.
[3] Plague buboes may turn black and necrotic, rotting away the surrounding tissue, or they may rupture, discharging large amounts of pus.
[3] Before the discovery of antibiotics, doctors often drained buboes with leeches or heated rods to save patients.
[6][7] In these conditions, a two-week course of antibiotics is the recommended treatment, and incision and drainage or excision of the swollen lymph nodes is best avoided.