James Webb Space Telescope
[9] This enables investigations across many fields of astronomy and cosmology, such as observation of the first stars and the formation of the first galaxies, and detailed atmospheric characterization of potentially habitable exoplanets.
[10][11][12] Although the Webb's mirror diameter is 2.7 times larger than that of the Hubble Space Telescope, it produces images of comparable sharpness because it observes in the longer-wavelength infrared spectrum.
[42] The Integrated Science Instrument Module (ISIM) is a framework that provides electrical power, computing resources, cooling capability as well as structural stability to the Webb telescope.
[43] NIRCam and MIRI feature starlight-blocking coronagraphs for observation of faint targets such as extrasolar planets and circumstellar disks very close to bright stars.
[49] The spacecraft bus is the primary support component of the JWST, hosting a multitude of computing, communication, electric power, propulsion, and structural parts.
These accommodations included precise guidance markers in the form of crosses on the surface of Webb, for use by remote servicing missions, as well as refillable fuel tanks, removable heat protectors, and accessible attachment points.
Another example is Hubble's Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) instrument, which started out using a block of nitrogen ice that depleted after a couple of years, but was then replaced during the STS-109 servicing mission with a cryocooler that worked continuously.
[81] In 1993, NASA conducted STS-61, the Space Shuttle mission that replaced HST's camera and installed a retrofit for its imaging spectrograph to compensate for the spherical aberration in its primary mirror.
"[82] Emboldened by HST's success, its 1996 report explored the concept of a larger and much colder, infrared-sensitive telescope that could reach back in cosmic time to the birth of the first galaxies.
As it matured, studying the birth of galaxies in the young universe, and searching for planets around other stars – the prime goals coalesced as "Origins" by HST & Beyond became prominent.
[85] An administrator of NASA, Dan Goldin, coined the phrase "faster, better, cheaper", and opted for the next big paradigm shift for astronomy, namely, breaking the barrier of a single mirror.
With the goal to reduce mass density tenfold, silicon carbide with a very thin layer of glass on top was first looked at, but beryllium was selected at the end.
The primary contractor was Northrop Grumman Aerospace Systems, responsible for developing and building the spacecraft element, which included the satellite bus, sunshield, Deployable Tower Assembly (DTA) which connects the Optical Telescope Element to the spacecraft bus, and the Mid Boom Assembly (MBA) which helps to deploy the large sunshields on orbit,[95] while Ball Aerospace & Technologies was subcontracted to develop and build the OTE itself, and the Integrated Science Instrument Module (ISIM).
[108] The review identified that Webb launch and deployment had 344 potential single-point failures – tasks that had no alternative or means of recovery if unsuccessful, and therefore had to succeed for the telescope to work.
[127] In summer 2010, the mission passed its Critical Design Review (CDR) with excellent grades on all technical matters, but schedule and cost slips at that time prompted Maryland U.S.
[142] For his role in improving the performance of the Webb program, Robinsons's supervisor, Thomas Zurbuchen, called him "the most effective leader of a mission I have ever seen in the history of NASA.
[152] A total of 258 companies, government agencies, and academic institutions participated in the pre-launch project; 142 from the United States, 104 from 12 European countries (including 21 from the U.K., 16 from France, 12 from Germany and 7 international),[153] and 12 from Canada.
The report found "no available evidence directly links Webb to any actions or follow-up related to the firing of individuals for their sexual orientation", either in his time in the State Department or at NASA.
[167] Because the thrusters are located solely on the Sun-facing side of the observatory, all station-keeping operations are designed to slightly undershoot the required amount of thrust in order to avoid pushing Webb beyond the semi-stable L2 point, a situation which would be unrecoverable.
Observations in infrared allow the study of objects and regions of space which would be obscured by gas and dust in the visible spectrum,[171] such as the molecular clouds where stars are born, the circumstellar disks that give rise to planets, and the cores of active galaxies.
[171] This includes the clouds of the interstellar medium, brown dwarfs, planets both in our own and other solar systems, comets, and Kuiper belt objects that will be observed with the Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI).
Data was to be transmitted from Webb to the ground via the NASA Deep Space Network, processed and calibrated at STScI, and then distributed online to astronomers worldwide.
[citation needed] The bandwidth and digital throughput of the satellite is designed to operate at 458 gigabits of data per day for the length of the mission (equivalent to a sustained rate of 5.42 Mbps).
NASA stated that the SIDECAR ASIC will include all the functions of a 9.1 kg (20 lb) instrument box in a 3 cm (1.2 in) package and consume only 11 milliwatts of power.
First, commands deployed the aft "momentum flap", a device that provides balance against solar pressure on the sunshield, saving fuel by reducing the need for thruster firing to maintain Webb's orientation.
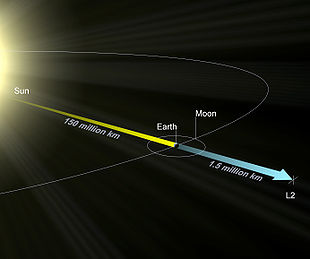
[208][209][210] On 24 January 2022, at 2:00 p.m. Eastern Standard Time,[211] nearly a month after launch, a third and final course correction took place, inserting Webb into its planned halo orbit around the Sun–Earth L2 point.
This mechanism is a grating wheel that allows scientists to select between short, medium, and longer wavelengths when making observations using the MRS mode," said NASA in a press statement.
The document described a series of observations during the commissioning, when the instruments captured spectra of transiting exoplanets with a precision better than 1000 ppm per data point, and tracked moving objects with speeds up to 67 milliarcseconds/second, more than twice as fast as the requirement.
Part of the JWST Advanced Deep Extragalactic Survey (JADES), this discovery highlights a galaxy significantly more luminous and massive than expected for such an early period.
[282] Occurring within the galaxy system ZS7, 740 million years after the Big Bang, this discovery suggests a fast growth rate for black holes through mergers, even in the young Universe.