CODASYL
This effort led to the development of the programming language COBOL, the CODASYL Data Model, and other technical standards.
It also worked on a wide range of other topics, including end-user form interfaces and operating system control languages, but these projects had little lasting impact.
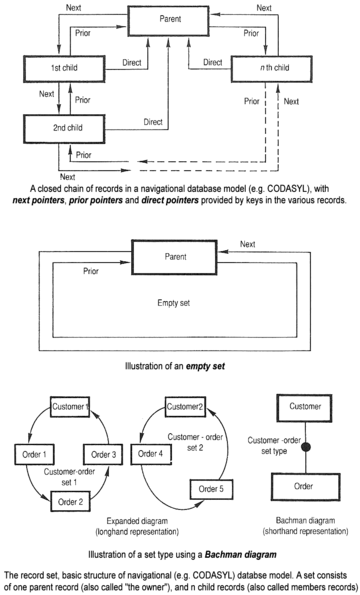
This group was chartered to develop COBOL language extensions for processing collections of records; the name arose because Charles Bachman's IDS system (which was the main technical input to the project) managed relationships between records using chains of pointers.
A number of vendors implemented database products conforming (roughly) to the DBTG specifications: the best-known implementations were Honeywell's—originally General Electric's—Integrated Data Store (IDS/2), HP's IMAGE, Cullinet's Integrated Database Management System IDMS, ICL's 2900 IDMS (derived from Cullinet's product), Univac's DMS-1100, and Digital Equipment Corporation's DBMS for VMS (later known as Oracle Codasyl DBMS).
Cullinet was eventually sold to Computer Associates, which as of 2007 still sells and supports a version of IDMS.